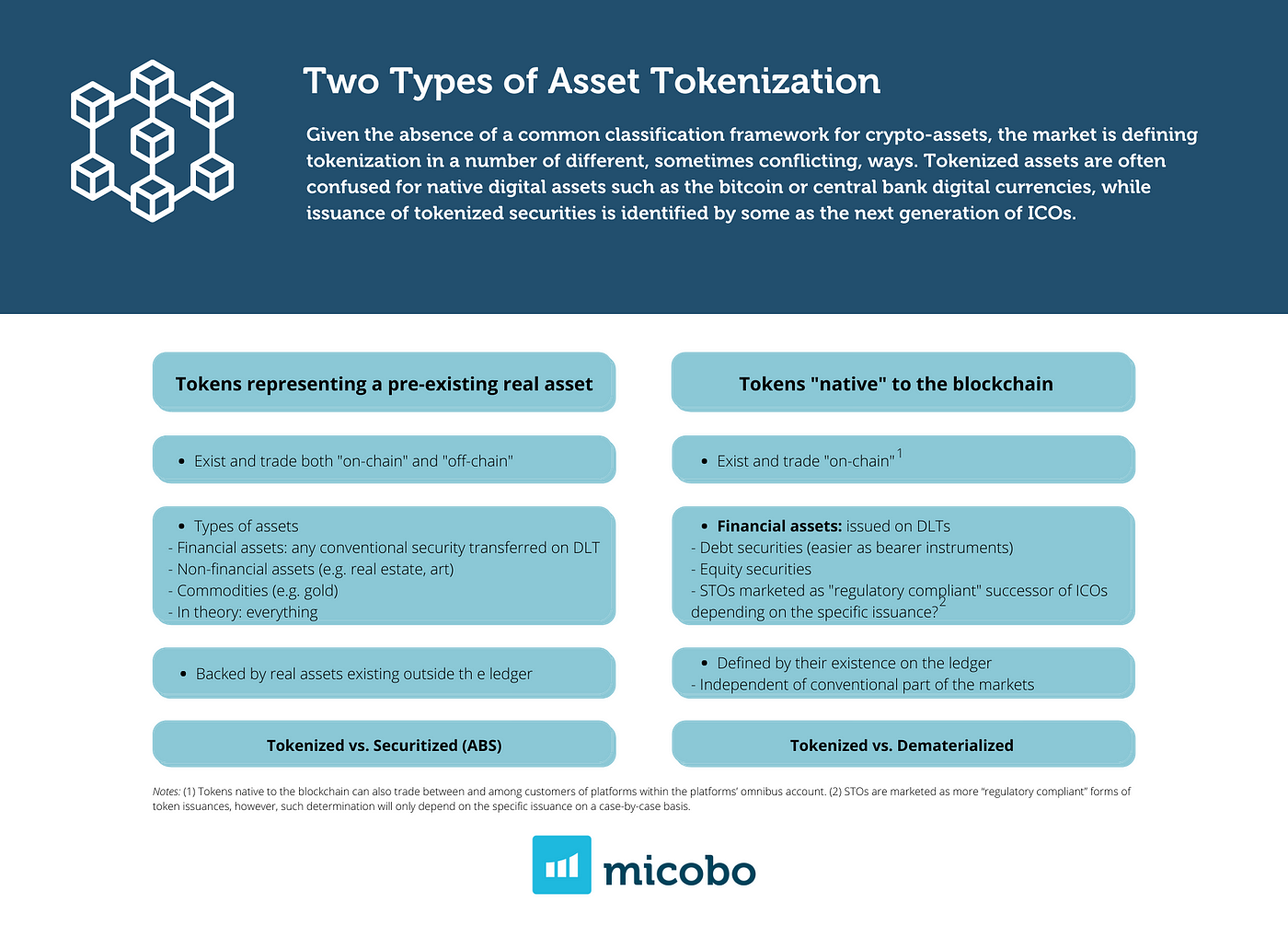
Maximizing Blockchain Efficiency: Scalability Solutions Unleashed

Maximizing Blockchain Efficiency: Scalability Solutions Unleashed
Blockchain technology has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, but as adoption increases, so do the challenges associated with scalability. In this ever-expanding landscape, addressing the scalability issue is paramount for blockchain networks to reach their full potential.
The Scaling Dilemma
Blockchain networks, especially popular ones like Bitcoin and Ethereum, face a bottleneck in transaction speed and cost. This challenge, commonly known as the scalability problem, hinders widespread adoption and efficient functionality. As more users join the network, the strain on resources becomes evident, necessitating innovative solutions.
Layer 2 Scaling: Building on Success
Layer 2 scaling solutions have emerged as a promising answer to the scalability challenge. These solutions operate on top of the main blockchain, alleviating congestion by handling transactions off-chain. Lightning Network for Bitcoin and various rollup solutions for Ethereum, such as Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups, showcase the potential of layer 2 scaling in significantly improving transaction throughput and reducing fees.
Off-Chain Scaling Techniques: Reducing On-Chain Burden
Off-chain scaling techniques take transactions off the main blockchain, aiming to reduce congestion and enhance scalability. Payment channels and state channels are prominent examples. Payment channels enable parties to conduct multiple transactions off-chain before settling on the main blockchain, while state channels provide a similar benefit for more complex interactions. These techniques contribute to faster and cost-effective transactions.
Sharding: Distributing the Load
Sharding is a groundbreaking concept designed to distribute the workload across multiple chains or shards. Each shard operates independently, processing its transactions, thereby enhancing the overall throughput of the network. Ethereum 2.0, currently in development, is set to implement sharding, providing a scalable solution to accommodate the growing demands on the network.
Plasma and Sidechains: Expanding Possibilities
Plasma and sidechains offer additional scalability avenues. Plasma chains are scalable and autonomous blockchain networks connected to the main chain. They provide a framework for creating child chains, reducing the burden on the primary network. Sidechains, on the other hand, operate independently while remaining interoperable with the main chain. Both Plasma and sidechains contribute to a more scalable and versatile blockchain ecosystem.
Optimistic Rollups: Balancing Speed and Security
Optimistic Rollups, a layer 2 scaling solution, prioritize transaction speed without compromising security. By batching transactions off-chain and submitting only the essential data to the main chain, Optimistic Rollups strike a balance between efficiency and maintaining the decentralized and secure nature of blockchain networks.
zk-Rollups: Zero-Knowledge Rollups for Enhanced Privacy
Zero-Knowledge Rollups, or zk-Rollups, prioritize privacy and scalability. Through the use of advanced cryptographic techniques, zk-Rollups allow for the verification of transactions without revealing their details. This not only enhances privacy but also contributes to a more scalable and efficient blockchain network.
Challenges on the Road to Scalability
While these scalability solutions bring promise, challenges remain. Adoption, implementation, and network-wide consensus are hurdles that must be overcome. Additionally, the need for interoperability between different scaling solutions and networks is crucial for a cohesive and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
Looking Ahead: A Scalable Future
As blockchain scalability solutions continue to evolve, the future holds promise for a more scalable and efficient decentralized digital landscape. The ongoing research, development, and implementation of these solutions mark significant strides toward realizing the full potential of blockchain technology. The journey to scalability is a dynamic one, and as challenges are met with innovative solutions, the vision of a scalable blockchain future becomes increasingly achievable.