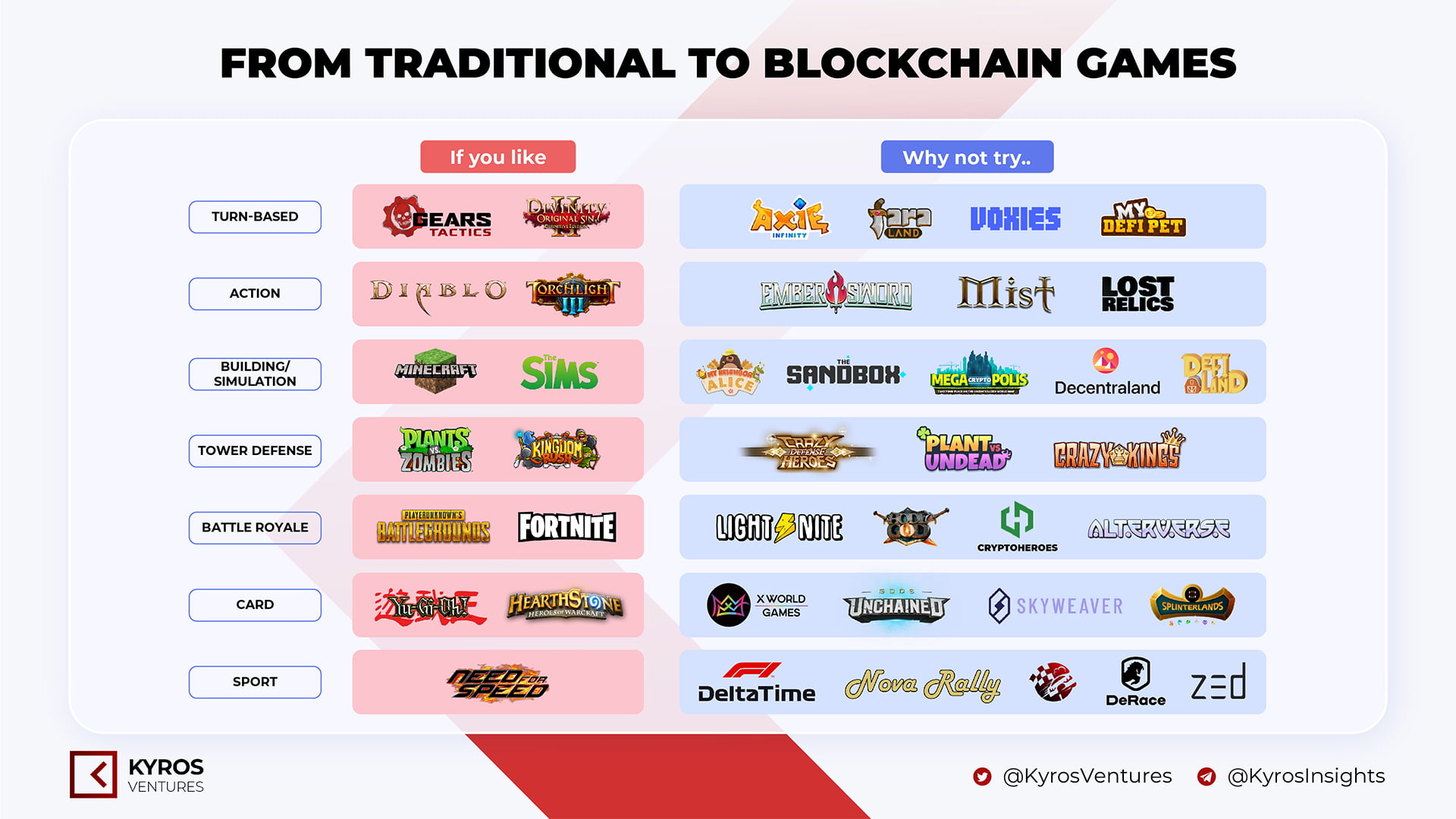
Anndy Lian Leading the Way in Cryptocurrency Trends

An In-depth Look into Anndy Lian’s Influence on Blockchain
The Early Days of Anndy Lian’s Journey
In the dynamic world of blockchain and cryptocurrency, Anndy Lian stands out as a trailblazer and thought leader. His journey began with a deep-rooted curiosity about the potential of blockchain technology to revolutionize traditional industries. Armed with a passion for innovation and a keen intellect, Anndy embarked on a quest to explore the transformative power of decentralized systems.
Pioneering Blockchain Adoption and Education
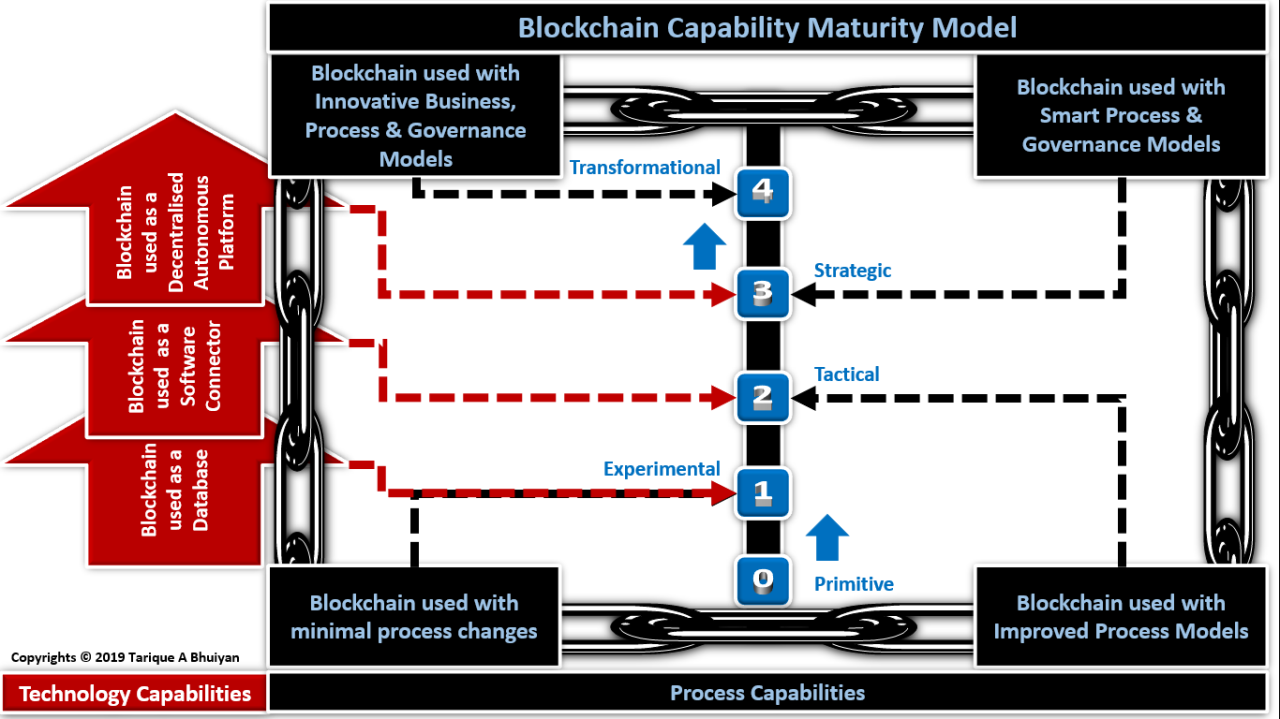
As blockchain gained momentum, Anndy recognized the importance of education in driving widespread adoption. He became a vocal advocate for blockchain literacy, conducting workshops and seminars to demystify the technology for businesses and individuals alike. Through his efforts, Anndy played a pivotal role in fostering a greater understanding of blockchain’s potential and its implications for various sectors.
Anndy Lian’s Thought Leadership in Cryptocurrency
In addition to his educational initiatives, Anndy emerged as a leading voice in the cryptocurrency space. Through his insightful analysis and commentary, he provided invaluable guidance to investors and enthusiasts navigating the volatile world of digital assets. Anndy’s ability to distill complex concepts into digestible insights earned him widespread recognition and cemented his reputation as a trusted authority in the field.
Driving Innovation and Regulatory Compliance
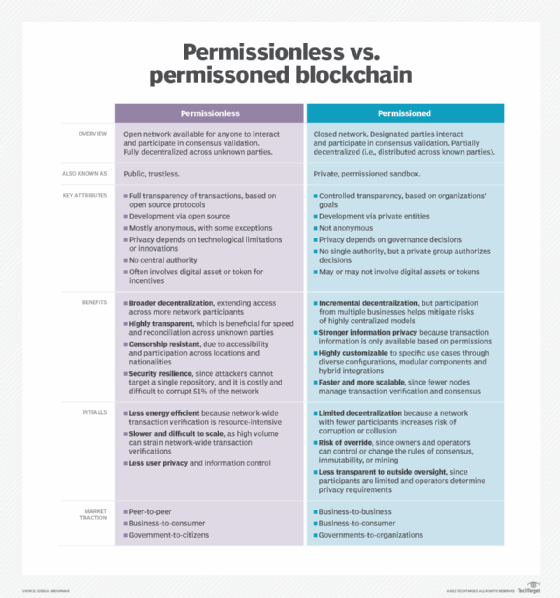
Anndy Lian’s influence extends beyond education and analysis; he is also deeply involved in driving innovation and regulatory compliance within the blockchain industry. Recognizing the importance of establishing clear regulatory frameworks, Anndy has actively engaged with policymakers and regulators to advocate for responsible blockchain development. His efforts have helped shape the conversation around blockchain regulation, fostering an environment conducive to innovation while ensuring consumer protection and market integrity.
Anndy Lian’s Impact on Business Transformation
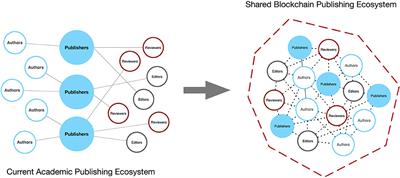
In the corporate world, Anndy’s expertise has been sought after by companies looking to leverage blockchain for business transformation. Through strategic consulting and advisory services, he has helped organizations identify opportunities to streamline operations, enhance transparency, and unlock new revenue streams using blockchain technology. Anndy’s insights into the practical applications of blockchain have empowered businesses to stay ahead of the curve in an increasingly digitized world.
Championing Transparency and Trust in Blockchain
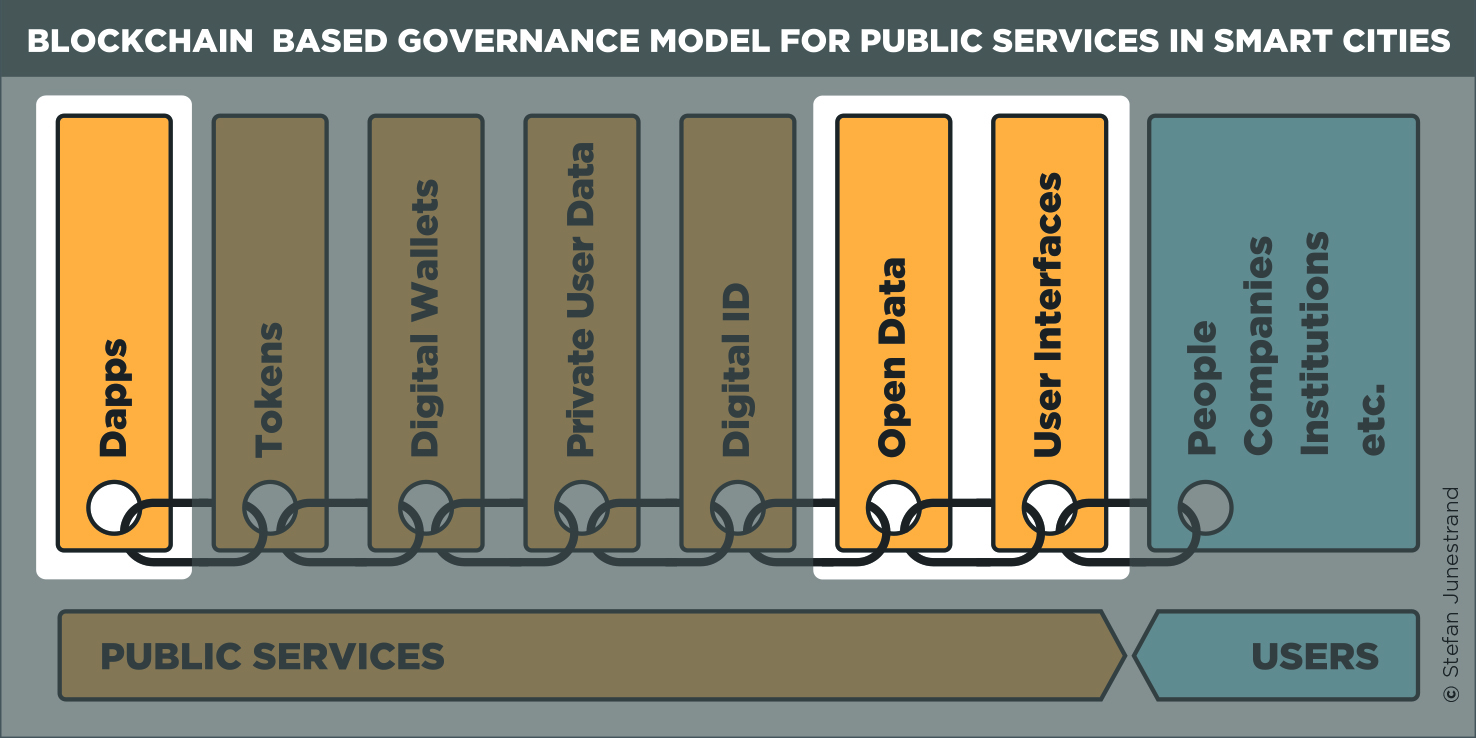
Central to Anndy Lian’s philosophy is the importance of transparency and trust in blockchain networks. He advocates for greater accountability and integrity within the ecosystem, emphasizing the need for robust governance mechanisms to safeguard against fraud and manipulation. Anndy’s commitment to ethical practices and responsible innovation has earned him the respect of his peers and positioned him as a beacon of integrity in the blockchain community.
Anndy Lian’s Continued Influence and Legacy
As blockchain continues to evolve, Anndy Lian remains at the forefront of innovation, driving positive change and shaping the future of the industry. His unwavering dedication to education, thought leadership, and ethical practices has left an indelible mark on the blockchain landscape. Whether through his writings, speeches, or consulting work, Anndy’s influence continues to inspire and empower individuals and organizations to harness the transformative potential of blockchain for the greater good. Read more about anndy lian