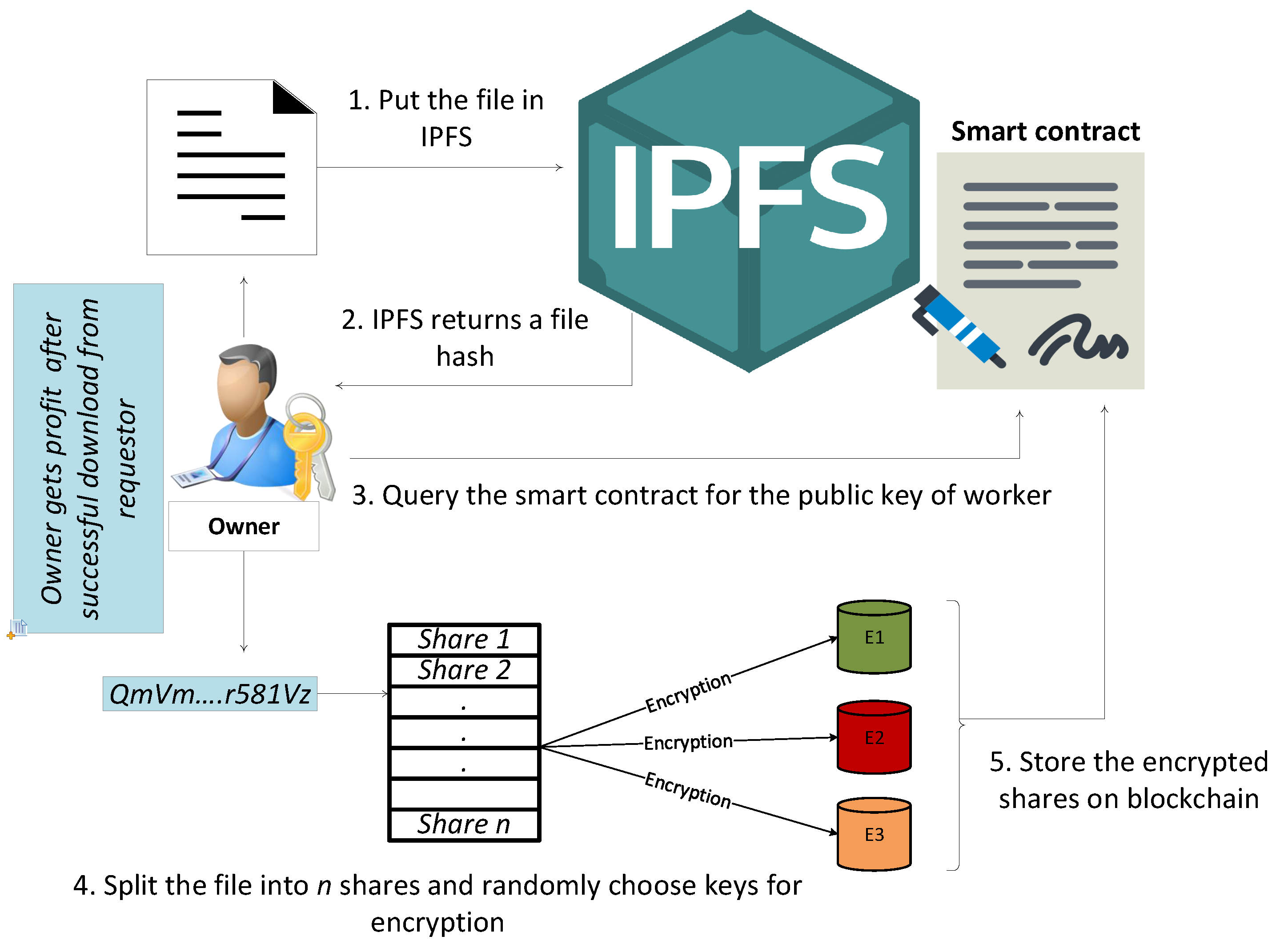
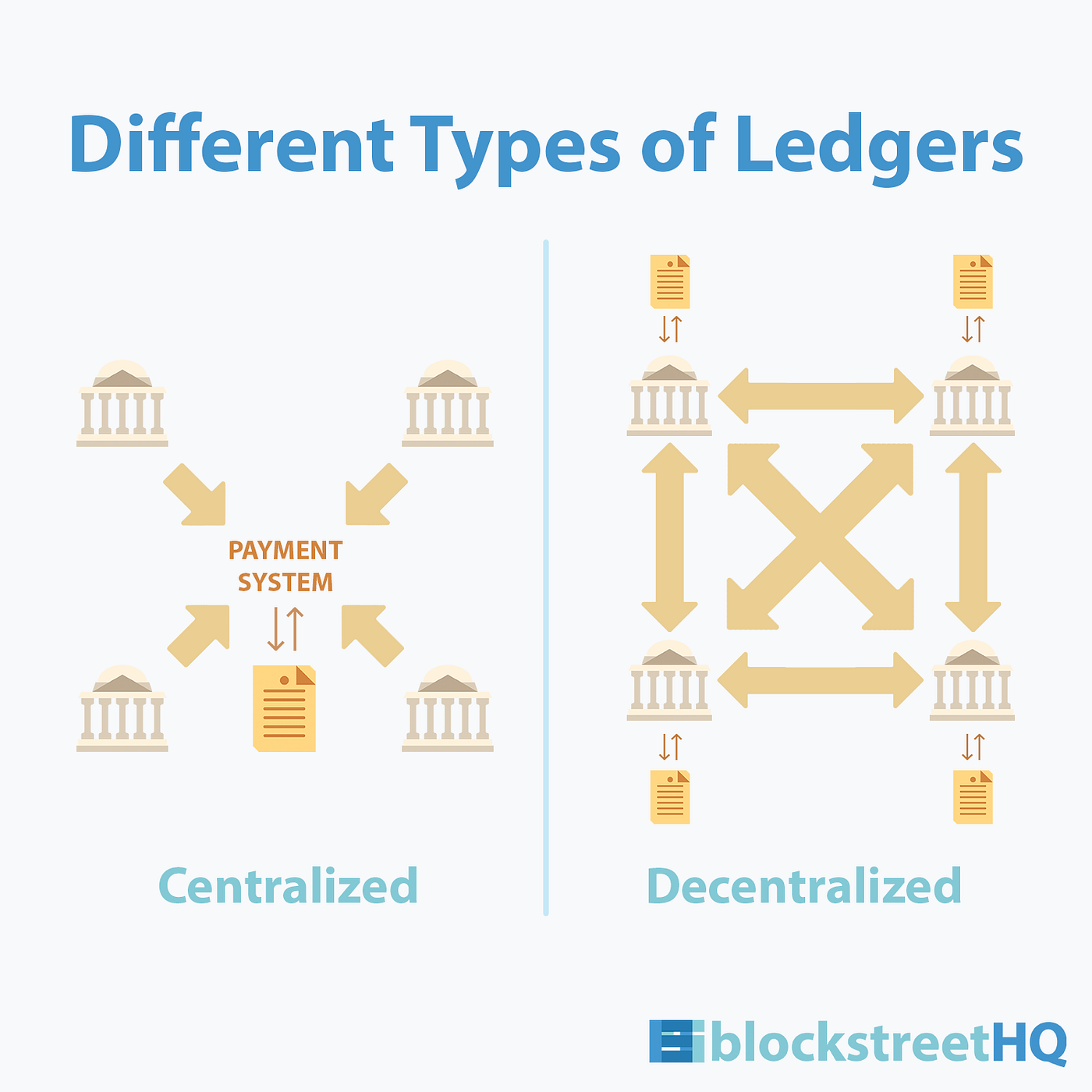
Decentralized Identity Solutions: Empowering Digital Autonomy

Introduction:
Decentralized identity solutions represent a paradigm shift in how individuals manage and control their digital identities. This article delves into the significance of decentralized identity solutions, their foundational principles, and the transformative impact they have on privacy, security, and user autonomy in the digital realm.
The Need for Digital Identity Transformation:
In the era of increasing digital interactions, the conventional model of centralized digital identities poses significant challenges. Issues like data breaches, identity theft, and the over-reliance on centralized authorities necessitate a fundamental transformation in how individuals assert and manage their identities online.
Principles of Decentralized Identity:
Decentralized identity solutions are built on principles of user-centricity, privacy, and security. Users have greater control over their personal information, choosing what to disclose and to whom. The elimination of central intermediaries reduces the risk of large-scale data breaches and puts individuals in the driver’s seat of their digital presence.
Blockchain Technology as the Enabler:
Blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in enabling decentralized identity solutions. The immutable and transparent nature of the blockchain ensures the integrity and security of identity-related data. Smart contracts and cryptographic techniques empower users to interact with services while maintaining control over their identity information.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI):
A key concept in decentralized identity is Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI). SSI empowers individuals with ownership and control over their digital identities without reliance on intermediaries. Through the use of decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials, SSI fosters a trustless and user-centric approach to identity management.
Interoperability Challenges and Solutions:
Interoperability is a critical aspect of decentralized identity solutions. Ensuring that different platforms and services can recognize and verify decentralized identities poses challenges. Standardization efforts, protocols like Decentralized Identity Foundation’s (DIF) specifications, and emerging technologies aim to address interoperability challenges and create a cohesive decentralized identity ecosystem.
Enhanced Security and Privacy:
Decentralized identity solutions enhance security and privacy by minimizing the exposure of sensitive information. Users can selectively disclose only the necessary details for a particular interaction without divulging their entire identity. The cryptographic underpinnings of decentralized identity add an extra layer of security, making it resistant to unauthorized access.
Use Cases Across Industries:
The applications of decentralized identity solutions extend across various industries. From healthcare and finance to education and beyond, decentralized identity offers a secure and efficient means of identity verification. Access to services, credentials, and personal information becomes more streamlined and user-controlled.
Challenges of Adoption:
While the potential of decentralized identity solutions is immense, widespread adoption faces hurdles. Overcoming challenges related to awareness, regulatory frameworks, and integration with existing systems is crucial. Collaborative efforts between the public and private sectors are essential to drive the adoption of decentralized identity on a global scale.
Decentralized Identity in Action:
Several projects and initiatives are actively implementing decentralized identity solutions. From open-source platforms to industry-specific applications, these initiatives showcase the versatility and real-world applicability of decentralized identity. Collaborative efforts foster innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the realm of digital identity.
Looking Ahead: Future of Decentralized Identity:
The future of decentralized identity holds promise for a more secure, user-centric, and globally interoperable digital identity ecosystem. Ongoing developments in blockchain technology, consensus mechanisms, and decentralized protocols will continue to shape the evolution of decentralized identity solutions, paving the way for a new era of digital autonomy.
To explore more about Decentralized Identity Solutions, visit here. Understanding the transformative potential of decentralized identity is crucial as we navigate the evolving landscape of digital interactions and the importance of safeguarding personal information in the digital age.