Open Gates: Navigating Permissionless Blockchain Platforms
Open Gates: Navigating Permissionless Blockchain Platforms
In the realm of blockchain technology, permissionless platforms stand out as pioneers, allowing open participation without the need for centralized control. This article delves into the dynamics of permissionless blockchain platforms, exploring their key features, use cases, and the impact they have on fostering a decentralized digital landscape.
Understanding Permissionless Blockchain Platforms
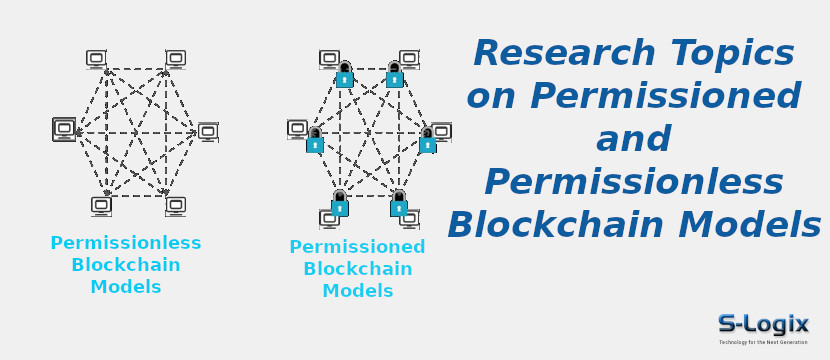
Permissionless blockchain platforms operate on the principle of inclusivity, enabling anyone to join and participate in the network without requiring approval. Unlike permissioned platforms that restrict access to a predetermined group, permissionless platforms embrace decentralization, offering transparency, security, and censorship resistance.
Key Features of Permissionless Platforms
The defining feature of permissionless blockchain platforms is their open nature. Participants, often referred to as nodes, can join the network, validate transactions, and contribute to the consensus process. The consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), are designed to be accessible to anyone willing to engage, ensuring a decentralized and trustless environment.
Decentralization and Censorship Resistance
Decentralization is a core principle of permissionless blockchain platforms. By distributing control across a network of nodes, these platforms mitigate the risk of a single point of failure and enhance security. Censorship resistance is a natural byproduct, as no central authority can dictate the inclusion or exclusion of participants or transactions.
Use Cases in Finance: Cryptocurrencies and DeFi
Permissionless blockchain platforms gained prominence with the introduction of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Bitcoin’s open and decentralized nature paved the way for permissionless financial transactions, allowing users to send and receive funds without intermediaries. The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) further expands the use cases, offering permissionless lending, borrowing, and trading.
Smart Contracts and DApps: Expanding Possibilities
Permissionless platforms, such as Ethereum, introduced the concept of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with coded terms. This innovation enables the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) that operate on the blockchain without central control. Smart contracts broaden the scope of permissionless platforms, facilitating programmable and automated transactions.
Challenges of Permissionless Platforms
While permissionless platforms offer numerous benefits, they face challenges. Scalability concerns, energy consumption in certain consensus mechanisms, and the potential for malicious activities are areas that require ongoing attention. Overcoming these challenges is essential for the sustained growth and adoption of permissionless blockchain platforms.
Innovation and Experimentation: The Open Playground
Permissionless platforms serve as an open playground for innovation and experimentation. Developers can explore new ideas, launch projects, and contribute to the evolution of the blockchain ecosystem. This dynamic environment fosters creativity and diversity, resulting in a rich tapestry of projects and protocols.
Community Governance and Decision-Making
Permissionless platforms often employ community governance models where participants have a say in the network’s evolution. Through proposals and voting mechanisms, the community collectively makes decisions on protocol upgrades, network improvements, and other crucial matters. This participatory approach enhances the resilience and adaptability of permissionless platforms.
The Role of Education and Accessibility
Educational initiatives play a crucial role in the adoption of permissionless blockchain platforms. By providing resources and tutorials, these platforms empower individuals to understand and engage with blockchain technology. Accessibility, both in terms of user-friendly interfaces and affordable hardware, is vital for broadening participation in permissionless networks.
Exploring Permissionless Blockchain Platforms – Learn More
To delve deeper into Permissionless Blockchain Platforms, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com. This comprehensive resource offers additional insights, tutorials, and updates on the latest developments in the world of permissionless blockchain and its impact on decentralized digital ecosystems.
In conclusion, permissionless blockchain platforms represent a paradigm shift towards decentralized and open systems. Their inclusive nature, coupled with innovations like smart contracts and decentralized finance, is reshaping how we interact with digital assets and services. As these platforms continue to evolve, they pave the way for a more inclusive and accessible digital future.