Scaling Beyond Limits: Exploring Layer 2 Solutions

Unlocking Scalability: Navigating the World of Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
The demand for scalable blockchain solutions has intensified as decentralized platforms gain popularity. Among the various approaches to scalability, Layer 2 scaling solutions have emerged as a promising strategy to enhance the throughput and efficiency of blockchain networks.
Understanding the Need for Scalability
As blockchain networks experience increased adoption, scalability becomes a crucial factor in their success. Traditional blockchains, such as Ethereum, face limitations in terms of transaction speed and cost. Layer 2 scaling solutions address these challenges by moving some of the transaction processing off the main blockchain, significantly improving performance.
The Concept of Layer 2 Scaling
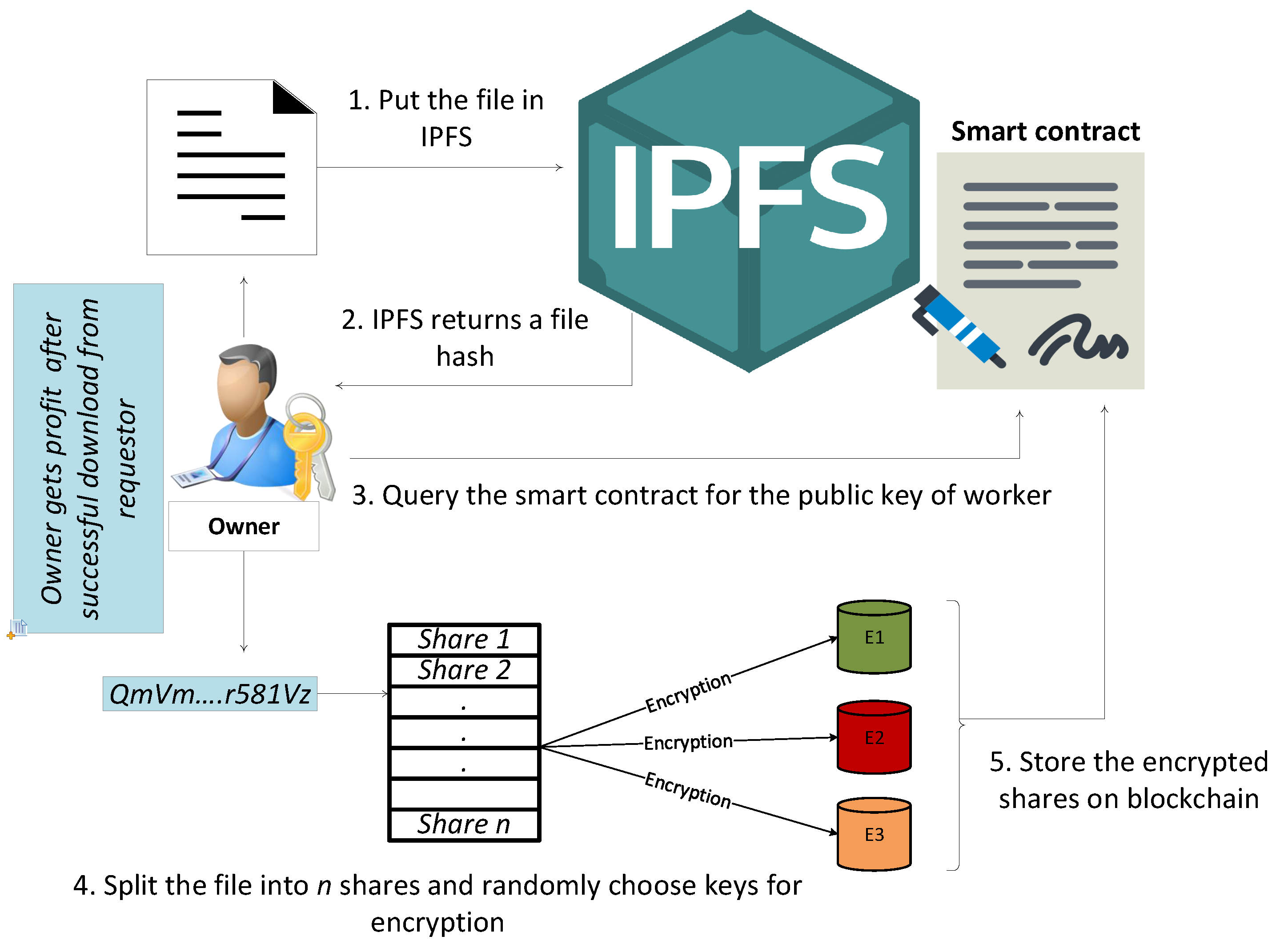
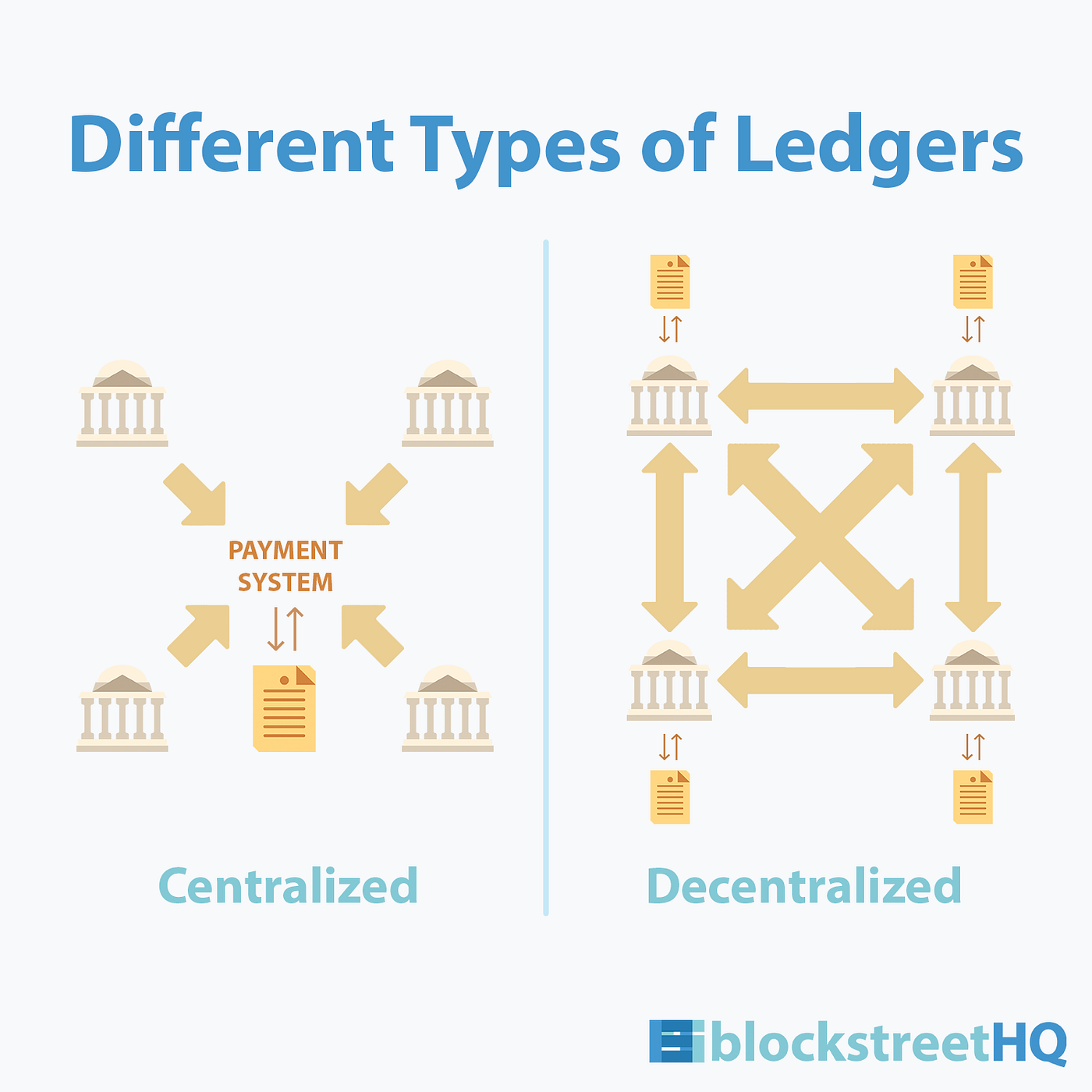
Layer 2 scaling involves creating secondary protocols or layers that operate on top of the primary blockchain. These layers facilitate faster and more cost-effective transactions by handling certain processes off-chain. This approach alleviates congestion on the main blockchain, resulting in a smoother and more scalable experience for users.
Different Approaches to Layer 2 Scaling
There are several Layer 2 scaling solutions, each employing unique techniques to optimize blockchain performance. Two prominent approaches are state channels and sidechains. State channels allow users to conduct off-chain transactions directly with each other, while sidechains are separate blockchains connected to the main chain, processing transactions independently.
Enhancing Transaction Speed and Lowering Costs
One of the primary advantages of Layer 2 scaling solutions is the significant boost in transaction speed and reduction in costs. By conducting transactions off-chain or on separate sidechains, the main blockchain is relieved of excessive processing, leading to quicker and more affordable transactions for users.
Improved Scalability without Compromising Security
While scalability is a top priority, security remains paramount in the blockchain space. Layer 2 scaling solutions are designed to uphold the security standards of the underlying blockchain. This ensures that users can enjoy the benefits of enhanced scalability without compromising the integrity and trustworthiness of the network.
Use Cases and Real-world Applications
Layer 2 scaling solutions have found practical applications in various blockchain projects. Gaming platforms, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, and non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces are leveraging these solutions to provide users with a seamless experience. The ability to process a high volume of transactions at a fraction of the cost opens up new possibilities for innovative blockchain applications.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising benefits, Layer 2 scaling solutions are not without challenges. Interoperability, user adoption, and the need for standardized protocols are areas that require careful consideration. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for the widespread adoption and success of Layer 2 scaling solutions.
The Road Ahead: Evolving Scalability Solutions
As the blockchain space continues to evolve, Layer 2 scaling solutions represent a critical component of the industry’s future. With ongoing developments and improvements, these solutions are expected to play a pivotal role in addressing the scalability trilemma – achieving decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously.
To explore more about Layer 2 Scaling Solutions, visit Layer 2 Scaling Solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Layer 2 scaling solutions offer a pathway to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology by addressing scalability challenges. By introducing secondary layers that enhance transaction speed, reduce costs, and maintain security, these solutions pave the way for a more scalable and efficient blockchain ecosystem. As the industry strives to accommodate growing user demands, Layer 2 scaling solutions stand as a testament to the innovative spirit driving blockchain development.