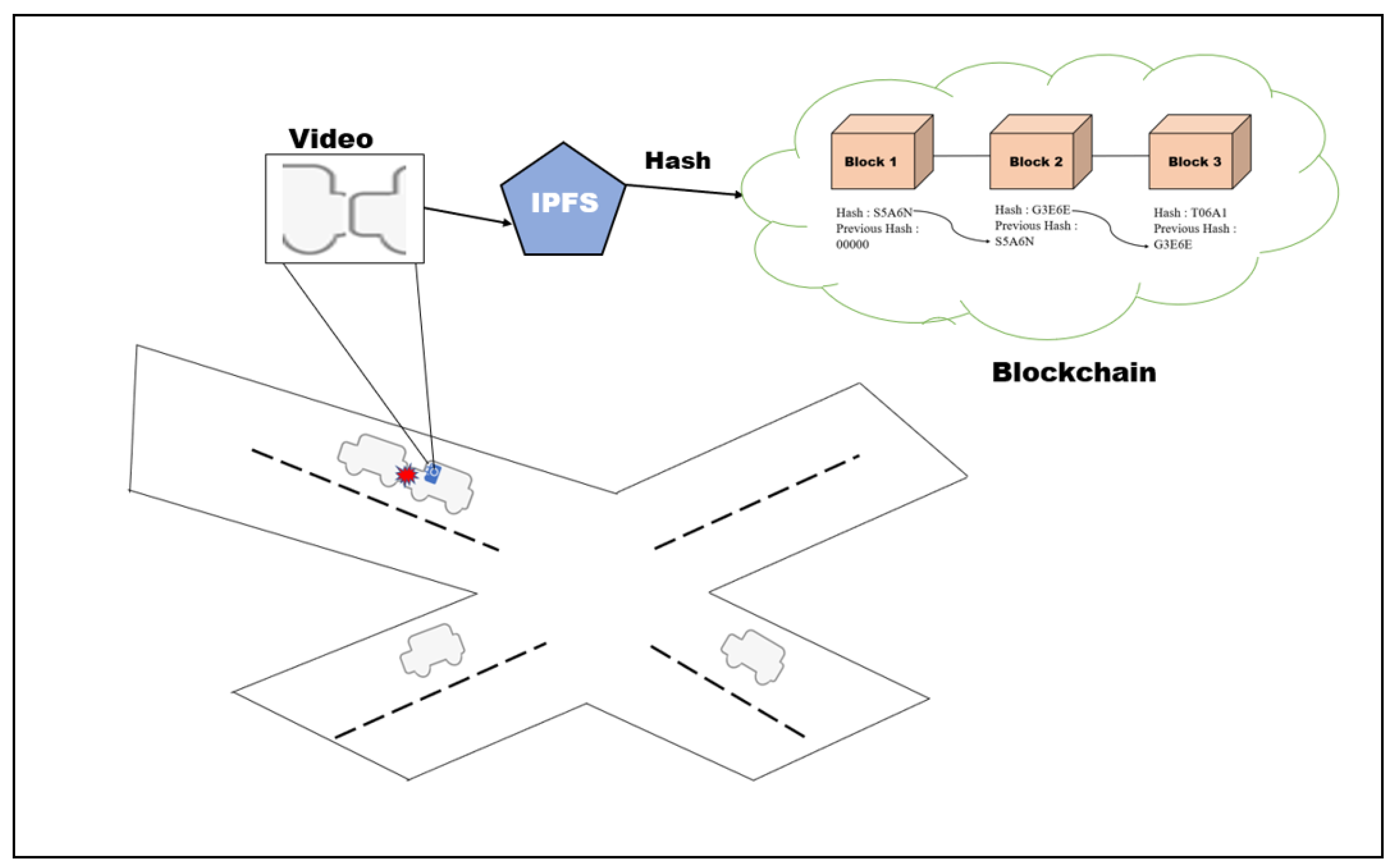
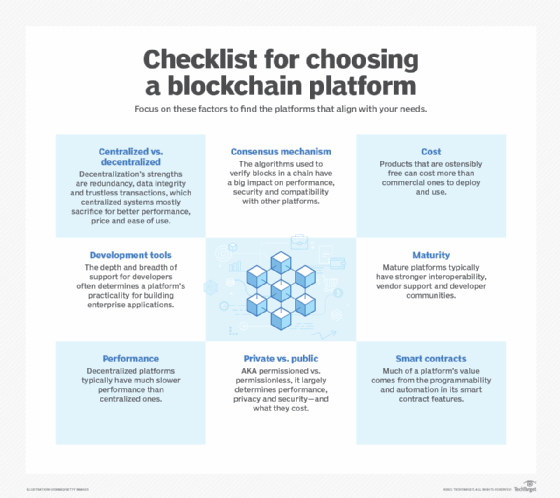
Blockchain Voting Mechanisms: Revolutionizing Electoral Processes
Introduction
The integration of blockchain technology into voting mechanisms is ushering in a new era of transparency, security, and accessibility in electoral processes. In this article, we delve into the transformative impact of Blockchain Voting Mechanisms and their potential to revolutionize the way we conduct elections.
Enhancing Security Through Decentralization
Traditional voting systems have often been vulnerable to hacking and manipulation. Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures that no single entity has control over the entire voting process. Each vote is securely recorded on a tamper-resistant ledger, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities and enhancing the overall security of the electoral system.
Immutable and Tamper-Resistant Records
One of the key advantages of blockchain technology is its immutability. Once a vote is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes a permanent and unchangeable part of the ledger. This feature provides an indelible record of each vote, instilling confidence in the integrity of the electoral process and allowing for transparent audits.
Ensuring Voter Privacy with Cryptography
Blockchain Voting Mechanisms leverage cryptographic techniques to ensure the privacy of individual voters. While each vote is recorded on the blockchain, the identity of the voter remains confidential. This balance between transparency and privacy addresses concerns related to coercion or the misuse of voter information.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Voting
Blockchain-based voting systems have the potential to increase accessibility and inclusivity in elections. With the ability to vote securely from any location with an internet connection, citizens who face barriers such as distance or physical limitations can participate more easily. This inclusivity promotes a more democratic and representative electoral process.
Smart Contracts Automating Election Processes
Smart contracts play a pivotal role in Blockchain Voting Mechanisms by automating various election processes. These self-executing contracts ensure that predefined rules and conditions are automatically enforced. Tasks such as voter eligibility verification, ballot counting, and result tabulation can be streamlined, reducing the likelihood of human error and disputes.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementation
While the potential benefits of Blockchain Voting Mechanisms are significant, challenges exist in their widespread adoption. Issues such as ensuring the security of the online voting platform, addressing technological literacy, and establishing a legal framework for blockchain-based elections require careful consideration and solutions.
Building Trust in Electoral Systems
Trust is paramount in any electoral process. Blockchain’s transparency, security features, and decentralized nature contribute to building trust among voters. By providing a verifiable and auditable record of every vote, blockchain technology can help restore faith in electoral systems and increase public confidence in the democratic process.
Educating Stakeholders and the Public
The successful implementation of Blockchain Voting Mechanisms necessitates educating various stakeholders, including election officials, policymakers, and the general public. Understanding the technology, its benefits, and its potential challenges is crucial for fostering acceptance and support for blockchain-based electoral systems.
Pilots and Real-World Applications
Several countries and organizations have initiated pilot projects to test the feasibility of Blockchain Voting Mechanisms. These real-world applications provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the technology, informing further development and refinement of blockchain-based electoral systems.
Looking to the Future of Democratic Processes
As technology continues to evolve, Blockchain Voting Mechanisms hold the promise of revolutionizing democratic processes worldwide. Their potential to provide secure, transparent, and accessible elections marks a significant step toward fostering a more inclusive and participatory democracy.
Explore more about Blockchain Voting Mechanisms at fireboyandwatergirlplay.com, where you can find additional resources and community discussions on the latest trends in blockchain technology and its applications in voting systems.