Safeguarding Data: Blockchain’s Privacy Protocols
Exploring Robust Blockchain Privacy Measures
Blockchain technology, renowned for its transparency and security, has been pivotal in reshaping digital landscapes. However, as industries increasingly rely on blockchain for sensitive transactions, the need for robust privacy measures becomes paramount.
Privacy Challenges in Blockchain
While the blockchain’s transparency is a strength, it poses challenges when dealing with confidential data. Traditional public blockchains expose transaction details to all participants, raising concerns about privacy, especially in sectors like finance and healthcare. Recognizing these challenges, developers have been actively working on implementing advanced privacy measures.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Unveiling Privacy without Exposure
One powerful tool in the blockchain privacy arsenal is zero-knowledge proofs. These cryptographic techniques enable one party (the prover) to prove the validity of a statement to another party (the verifier) without revealing any information about the statement itself. This breakthrough technology allows for transactions to be confirmed without disclosing the transaction details, ensuring data confidentiality.
Ring Signatures and Confidential Transactions
In addition to zero-knowledge proofs, blockchain privacy measures often involve ring signatures and confidential transactions. Ring signatures allow a user to sign a transaction on behalf of a group, making it indistinguishable who within the group signed it. Confidential transactions, on the other hand, obscure the transaction amount, enhancing privacy by preventing external parties from deducing financial details.
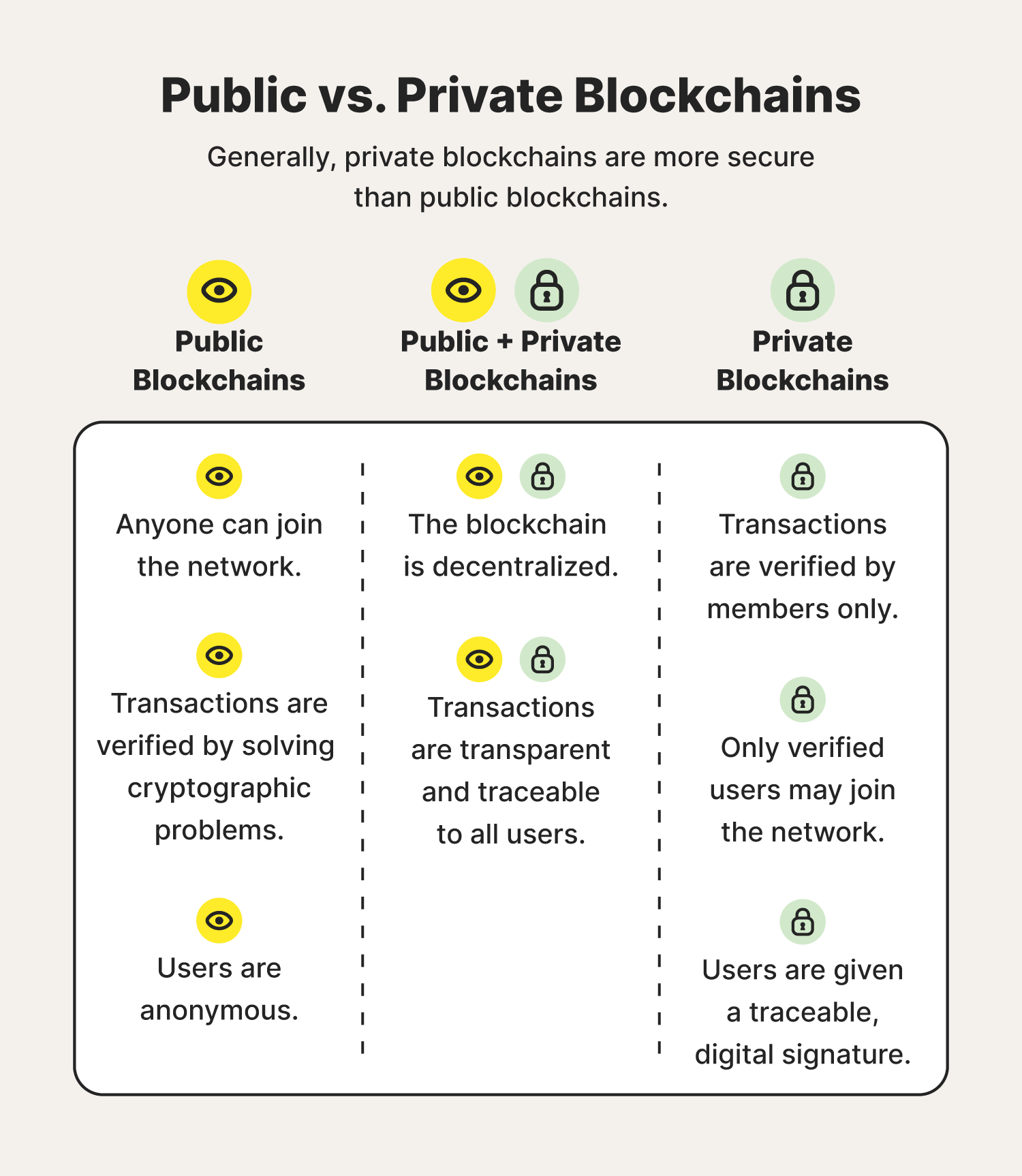
The Role of Private Blockchains
Private blockchains, unlike their public counterparts, restrict access to a predefined set of participants. This inherent exclusivity ensures that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized users. Industries with stringent privacy requirements, such as healthcare and government, find private blockchains to be an ideal solution, combining the benefits of blockchain technology with controlled access.
Decentralized Identity and Privacy
Decentralized identity solutions contribute significantly to enhancing privacy on the blockchain. By enabling users to have control over their identity and personal information, decentralized identity systems mitigate the risks associated with centralized data repositories. Users can selectively disclose information, reducing the exposure of sensitive data.
Blockchain Privacy in Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, integral to blockchain functionality, also benefit from privacy enhancements. Solutions like zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge) enable the execution of smart contracts without revealing specific inputs or outputs. This ensures that contract details remain confidential while still achieving the desired outcomes.
The Ongoing Evolution of Privacy Measures
Blockchain’s quest for privacy is an ongoing evolution. New technologies and consensus mechanisms are continually being developed to strike the delicate balance between transparency and confidentiality. As blockchain finds its way into more industries, the demand for enhanced privacy measures is expected to drive innovation in this space.
To delve deeper into the world of blockchain privacy measures and their applications, explore Blockchain Privacy Measures.
In conclusion, the integration of robust privacy measures is essential for blockchain’s continued success in handling sensitive data. Zero-knowledge proofs, private blockchains, decentralized identity, and evolving technologies collectively contribute to fostering a secure and confidential environment on the blockchain. As industries adapt to these advancements, the potential applications of blockchain technology in privacy-sensitive sectors continue to expand.