Off-Chain Data Oracles: Enhancing Blockchain Accuracy
Enhancing Blockchain Accuracy: Exploring Off-Chain Data Oracle Solutions
Blockchain’s decentralized nature is a cornerstone of its reliability, but it faces challenges when interacting with real-world data. Off-chain data oracle solutions play a pivotal role in bridging this gap, ensuring accurate and reliable information integration into blockchain networks.
Understanding the Need for Off-Chain Data Oracles
Blockchain networks operate in a closed environment, isolated from external data sources. While this isolation ensures security and trust, it poses a challenge when blockchain applications require real-world data, such as weather conditions, market prices, or sports scores. Off-chain data oracles serve as bridges, bringing external information into the blockchain in a secure and decentralized manner.
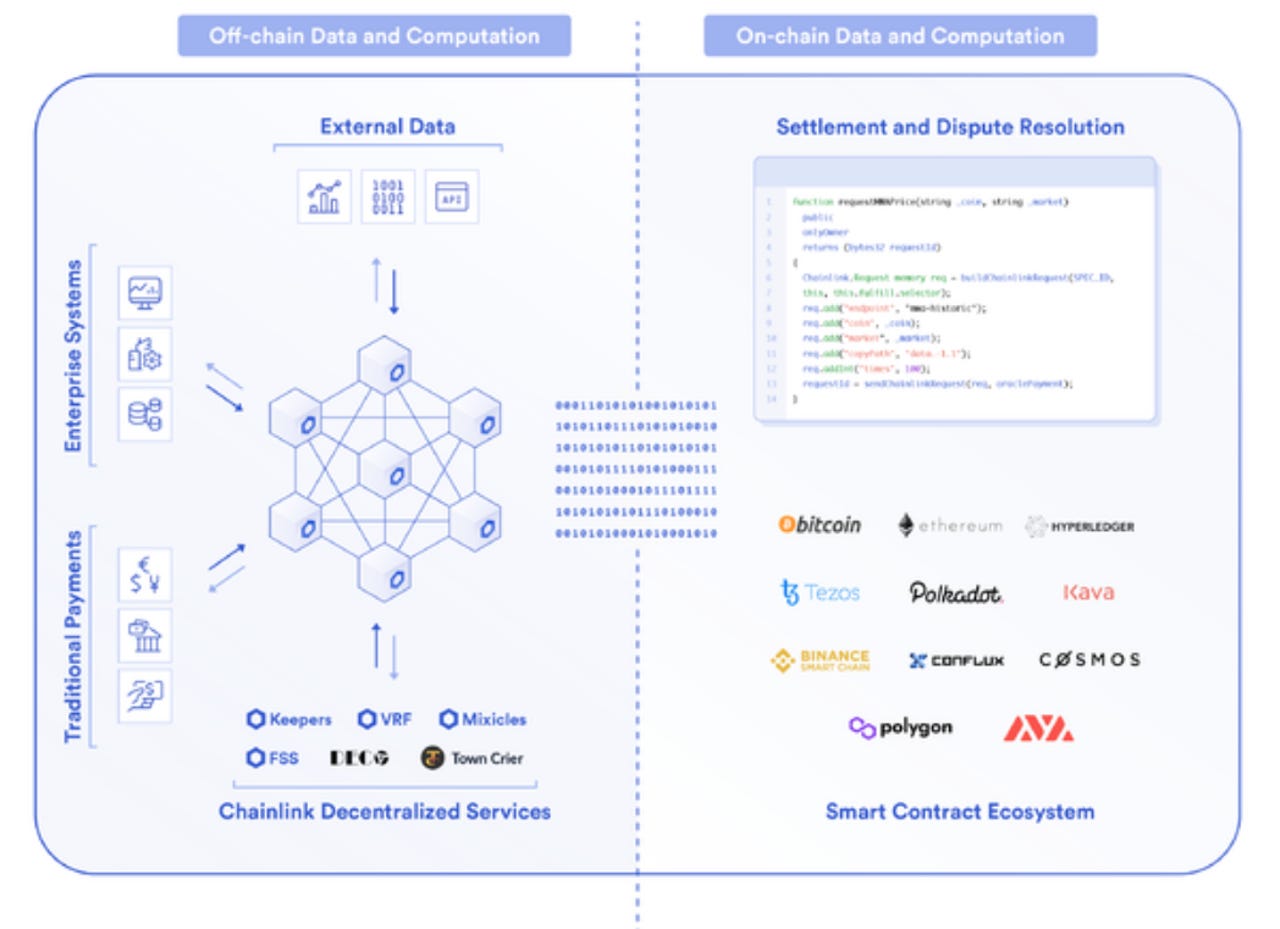
How Off-Chain Data Oracles Work
Off-chain data oracles act as middleware, connecting smart contracts with real-world data. These oracles collect and verify information from various sources, ensuring its accuracy before transmitting it to the blockchain. This verification process is crucial to prevent misinformation or manipulation, maintaining the integrity of the blockchain-based application.
Types of Off-Chain Data Oracles
There are two main types of off-chain data oracles: centralized and decentralized. Centralized oracles rely on a single source for data, making them susceptible to manipulation. Decentralized oracles, on the other hand, aggregate information from multiple sources and use consensus mechanisms to validate data accuracy, providing a more reliable solution for blockchain applications.
Securing Data Integrity through Decentralization
Decentralized off-chain data oracles mitigate the risk of a single point of failure. By distributing data collection and validation across a network of nodes, these oracles enhance security and reduce the vulnerability to malicious attacks or inaccuracies from a single source. This decentralization aligns with the core principles of blockchain technology.
Challenges and Solutions in Off-Chain Oracle Implementations
Despite their benefits, implementing off-chain data oracles comes with challenges. Security concerns, data tampering risks, and the need for trust in external data sources are among the issues. Solutions involve implementing robust security measures, utilizing multiple data sources, and incorporating consensus mechanisms to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
Use Cases for Off-Chain Data Oracle Solutions
Off-chain data oracles find application in various industries. From decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms relying on accurate price feeds to supply chain management systems tracking real-world events, the versatility of these solutions enhances the functionality and practicality of blockchain applications in the broader ecosystem.
Integration with Smart Contracts and DApps
Off-chain data oracles seamlessly integrate with smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Smart contracts execute predefined actions based on specific conditions, and off-chain data oracles provide the necessary information to trigger these actions. This integration expands the scope of blockchain applications, enabling them to interact with real-world events and conditions.
The Role of Off-Chain Data Oracles in Decentralized Finance
Decentralized finance relies heavily on accurate and timely data. Off-chain data oracles play a vital role in providing DeFi platforms with real-world information, such as cryptocurrency prices and market conditions. This data is critical for executing smart contracts related to lending, borrowing, and trading on DeFi platforms.
Future Developments and Industry Adoption
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the role of off-chain data oracles is expected to expand. The industry is witnessing advancements in oracle technology, addressing existing challenges and improving overall efficiency. Increased adoption of blockchain and decentralized applications across various sectors further emphasizes the need for reliable off-chain data solutions.
Exploring Off-Chain Data Oracle Solutions – Learn More
To delve deeper into Off-Chain Data Oracle Solutions, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com. This comprehensive resource offers additional insights, tutorials, and updates on the latest developments in the world of off-chain data oracles and their impact on blockchain applications.
In conclusion, off-chain data oracles play a crucial role in enhancing the accuracy and functionality of blockchain applications. As blockchain technology becomes more integrated into real-world scenarios, the need for reliable external data sources grows. Off-chain data oracle solutions bridge this gap, ensuring that blockchain networks can interact seamlessly with the dynamic and ever-changing external world.








