Consensus Algorithm Comparison: Navigating Blockchain Validation
Introduction
Consensus algorithms lie at the heart of blockchain networks, determining how nodes agree on the state of the distributed ledger. In this article, we delve into the world of consensus algorithm comparison, exploring the different approaches that underpin the validation process in blockchain technology.
Understanding Consensus Algorithms
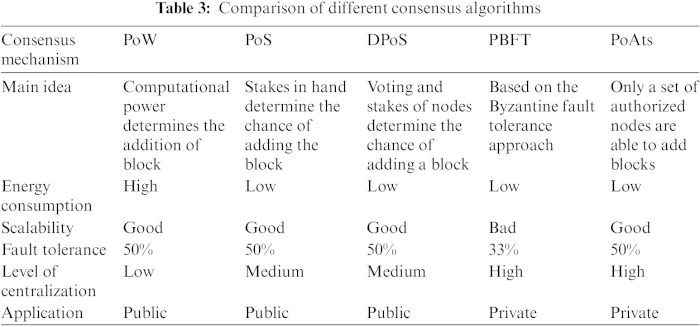
Consensus algorithms are the mechanisms that enable nodes in a decentralized network to agree on the state of the blockchain. Various consensus models, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (PoS), and Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), differ in their approach to achieving agreement. Understanding the intricacies of these models is crucial for making informed decisions in blockchain design.
Proof-of-Work: The Pioneer
Proof-of-Work, known as the pioneer consensus algorithm, requires participants (miners) to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. While PoW is renowned for its security, it comes with drawbacks, including high energy consumption and scalability challenges.
Proof-of-Stake: Shifting the Paradigm
In contrast, Proof-of-Stake replaces the competitive aspect of mining with a deterministic process based on the amount of cryptocurrency held by participants. This approach aims to reduce energy consumption and increase scalability. PoS introduces economic incentives for validators, aligning their interests with the stability of the network.
Delegated Proof-of-Stake: Efficiency Through Delegation
Delegated Proof-of-Stake builds upon PoS by introducing a select group of validators known as delegates. These delegates are elected by coin holders to validate transactions and produce blocks. DPoS enhances scalability and efficiency by reducing the number of participants involved in the consensus process.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance: Ensuring Byzantine Agreement
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) focuses on achieving consensus in the presence of faulty nodes. It requires a two-thirds majority for nodes to agree on the validity of transactions. PBFT is often favored in permissioned blockchains where the number of participants is known and controlled.
Comparison Metrics: Security, Scalability, and Decentralization
When comparing consensus algorithms, several metrics come into play. Security, scalability, and decentralization are critical factors. PoW is celebrated for its robust security, but at the expense of scalability. PoS and DPoS aim to address scalability concerns but may raise questions about decentralization due to the concentration of power.
Emerging Trends: Hybrid Models and Innovations
As blockchain technology evolves, new consensus models and hybrid approaches continue to emerge. Some projects explore combinations of existing algorithms to leverage their strengths and mitigate weaknesses. These innovations strive to find a balance between security, scalability, and decentralization.
Real-World Applications: Tailoring Consensus to Use Cases
The choice of consensus algorithm depends on the specific use case of the blockchain. Public networks may prioritize decentralization and security, while private or consortium blockchains might favor efficiency and scalability. Tailoring the consensus mechanism to the application is essential for optimal performance.
Consensus Algorithm Comparison: A Holistic View
In conclusion, the landscape of consensus algorithms is diverse, each with its advantages and challenges. A holistic view that considers the unique requirements of a blockchain project is necessary when choosing the most suitable consensus mechanism. Explore more on Consensus Algorithm Comparison at fireboyandwatergirlplay.com, where you can find additional resources and community discussions on the latest trends in blockchain technology.








