Governed Blockchains: Navigating Permissioned Networks
Unlocking the Potential of Governed Blockchains
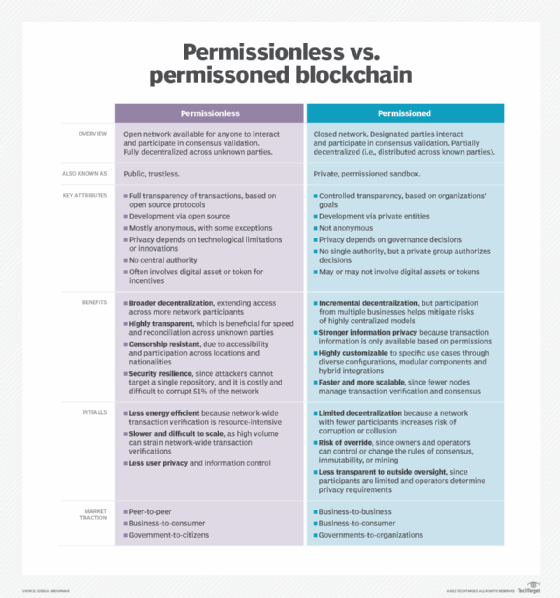
In the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology, permissioned blockchain networks stand out as a strategic approach to balance decentralization with governance. Unlike their permissionless counterparts, permissioned blockchains introduce a layer of control over participants, making them suitable for various enterprise applications and specific use cases.
Defining Permissioned Blockchains: A Governance Approach
Permissioned blockchains, as the name suggests, require participants to obtain explicit permission to join the network. This stands in contrast to permissionless blockchains like Bitcoin, where anyone can participate without restriction. The permissioned approach allows for a more structured governance model, making it an attractive option for businesses and organizations seeking to leverage blockchain technology while maintaining control.
Governance Structures in Permissioned Blockchains
One of the key advantages of permissioned blockchain networks is the ability to implement tailored governance structures. Participants in these networks often include known and trusted entities, allowing for the establishment of clear rules and decision-making processes. This governance framework enhances accountability, making permissioned blockchains suitable for industries with regulatory requirements or specific compliance needs.
Enhanced Privacy and Confidentiality
Permissioned blockchains prioritize privacy and confidentiality, addressing concerns that have arisen with permissionless networks. With controlled access, participants can share sensitive information within the blockchain while ensuring that only authorized parties have visibility. This feature makes permissioned blockchains appealing to sectors such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain, where data privacy is paramount.
Consortium Blockchains: Collaboration and Shared Control
Within the realm of permissioned blockchains, consortium blockchains shine as a collaborative model. In a consortium blockchain, multiple organizations come together to share control over the network. This collaborative approach fosters efficiency, reduces duplication of efforts, and enables secure data sharing among consortium members. It’s a testament to how permissioned blockchains can facilitate industry-wide cooperation.
Use Cases: Industries Embracing Permissioned Blockchains
Permissioned blockchain networks find applications across various industries. Financial institutions deploy them for streamlined transactions and improved auditability. Healthcare providers utilize them to enhance patient data management securely. Supply chain networks leverage permissioned blockchains for traceability and transparency. These examples highlight the adaptability and versatility of permissioned blockchains in real-world scenarios.
Addressing Scalability and Performance
Permissioned blockchains often exhibit superior scalability and performance compared to their permissionless counterparts. With a controlled number of participants and a predefined consensus mechanism, these networks can process transactions more efficiently. This makes permissioned blockchains suitable for applications that demand high throughput and rapid transaction confirmation.
Challenges and Considerations
While permissioned blockchains offer advantages in certain contexts, they are not without challenges. Striking the right balance between decentralization and control requires careful consideration. Interoperability with other networks and ensuring ongoing participant engagement are aspects that demand attention. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for maximizing the potential of permissioned blockchains.
Future Prospects: Evolving Governance and Innovation
The evolution of permissioned blockchains continues as industries recognize their potential. Innovations in governance models, consensus mechanisms, and interoperability protocols are underway. The future promises increased customization, allowing organizations to tailor permissioned blockchain networks to their specific needs while staying abreast of technological advancements.
Exploring Governed Blockchains: A Call to Action
To delve deeper into the world of permissioned blockchain networks, explore Permissioned Blockchain Networks. Discover the governance structures, industry applications, and evolving innovations that shape the landscape of governed blockchains. It’s an invitation to understand, engage, and navigate the exciting developments in the realm of blockchain technology.