Permissionless Blockchain Platforms: Unleashing Decentralized Potential
Introduction:
Permissionless blockchain platforms have become synonymous with the democratization of digital ecosystems, offering a decentralized approach to various industries. This article explores the concept of permissionless blockchain platforms, their fundamental principles, and the impact they have on fostering innovation and inclusivity.
Decentralization at the Core:
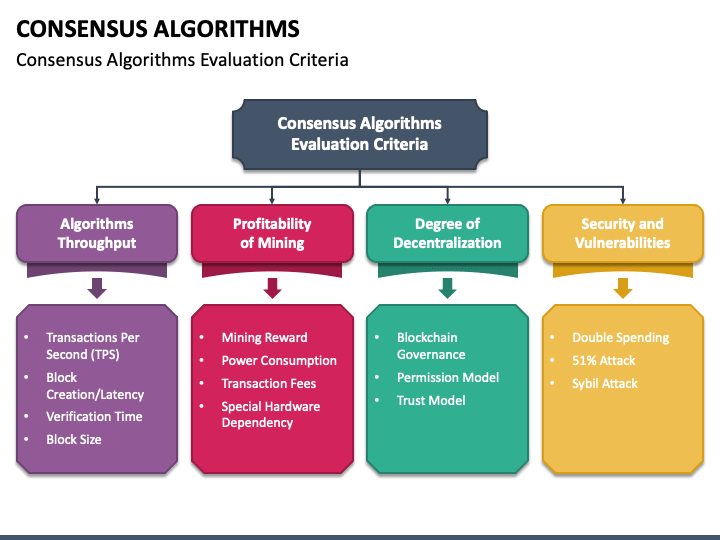
Permissionless blockchain platforms prioritize decentralization as a core principle. Unlike their permissioned counterparts, where access is restricted to a select group, permissionless blockchains allow anyone to participate in the network. This inclusivity is achieved through open access and a consensus mechanism that empowers participants to validate transactions and contribute to the network’s security.
Innovative Consensus Mechanisms:
One hallmark of permissionless blockchain platforms is the utilization of innovative consensus mechanisms. Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are common examples. These mechanisms ensure that participants, often referred to as nodes or miners, collectively agree on the state of the blockchain. This decentralized agreement process is fundamental to the security and integrity of the permissionless blockchain.
Cryptocurrency Creation and Tokenization:
Permissionless blockchains often serve as the foundation for the creation of cryptocurrencies and tokenized assets. Through a process known as Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) or Token Generation Events (TGEs), projects can fundraise and distribute tokens to a global audience. This democratized funding model has allowed for the emergence of diverse blockchain-based projects.
Open Participation and Accessibility:
One of the key advantages of permissionless blockchain platforms is their open participation and accessibility. Anyone with an internet connection can join the network, validate transactions, and even propose changes to the protocol. This inclusivity fosters a global community of developers, validators, and users contributing to the platform’s growth and evolution.
Challenges of Scalability:
While permissionless blockchains offer unparalleled decentralization, they face challenges related to scalability. As the user base and transaction volume grow, maintaining high throughput becomes a concern. Various scaling solutions, including layer-two protocols and consensus upgrades, are being explored to address these challenges and enhance the scalability of permissionless blockchain platforms.
Community Governance and Decision-Making:
Community governance is a distinctive feature of permissionless blockchain platforms. Decisions regarding protocol upgrades, changes, and future developments are often made through community-wide consensus. Token holders and active participants have a say in the governance process, creating a democratic framework that aligns with the decentralized ethos of these platforms.
Use Cases Beyond Cryptocurrencies:
While permissionless blockchains gained prominence with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, their use cases extend far beyond digital currencies. Decentralized applications (DApps), smart contracts, and tokenized assets are transforming industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, and more. Permissionless blockchain platforms provide the infrastructure for these innovative solutions.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Revolution:
Permissionless blockchain platforms play a pivotal role in the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) revolution. Through smart contracts and open financial protocols, DeFi platforms offer a range of financial services, including lending, borrowing, and decentralized trading. This democratized approach to finance empowers users and reduces reliance on traditional financial intermediaries.
Looking Ahead: Future Developments:
The landscape of permissionless blockchain platforms is dynamic, with ongoing developments and future trends shaping their trajectory. Innovations such as sharding, improved consensus algorithms, and enhanced privacy features are on the horizon. Staying abreast of these advancements is essential for participants in the permissionless blockchain space.
To explore more about Permissionless Blockchain Platforms, visit here. The openness and decentralization of permissionless blockchains continue to redefine how we interact with digital systems, offering a glimpse into a future where decentralized networks drive innovation, inclusivity, and global collaboration.