Navigating Consensus: Evaluating Blockchain Algorithms for Efficiency
Deciphering the Significance of Consensus Algorithm Evaluation
In the dynamic realm of blockchain technology, the efficiency of consensus algorithms is paramount. Consensus algorithms lay the foundation for the security, scalability, and performance of blockchain networks. Evaluating these algorithms becomes a crucial exercise in ensuring the optimal functioning of decentralized systems.
Understanding Consensus Algorithms in Blockchain
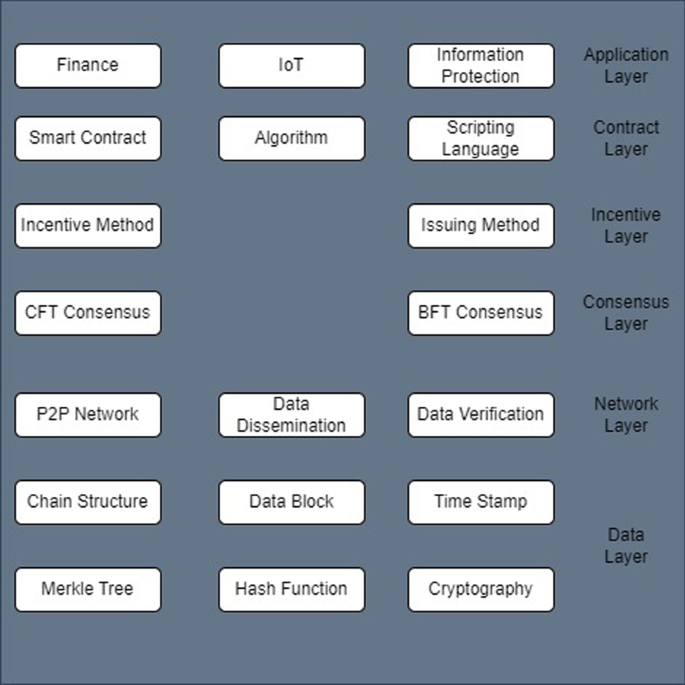
Consensus algorithms serve as the mechanism by which participants in a blockchain network agree on the state of the ledger. From the pioneering Proof-of-Work (PoW) to newer models like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), each algorithm comes with its strengths and limitations. Understanding their nuances is fundamental to making informed choices in blockchain design.
Scalability Challenges and Consensus
As blockchain networks expand and the number of transactions increases, scalability becomes a critical consideration. Different consensus algorithms handle scalability challenges differently. Some, like sharding in Proof-of-Stake systems, aim to parallelize transaction processing, enhancing the network’s capacity. Consensus algorithm evaluation is vital in identifying the most scalable solution for specific use cases.
Security Implications of Consensus Choices
Consensus algorithm evaluation also delves into the security implications of different models. While PoW is renowned for its robust security due to the computational effort required to mine blocks, PoS introduces economic security by tying influence to the ownership of cryptocurrency. Understanding the trade-offs between these security models is essential in maintaining the integrity of a blockchain network.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Concerns
The environmental impact of consensus algorithms, particularly evident in PoW-based blockchains like Bitcoin, has sparked discussions on the need for more energy-efficient alternatives. PoS and other consensus models offer a greener approach by not requiring the massive computational power associated with PoW. Consensus algorithm evaluation weighs the environmental sustainability of different choices.
Decentralization vs. Efficiency Dilemma
Consensus algorithms often involve a delicate balance between decentralization and efficiency. PoW, while decentralized, can be resource-intensive. PoS models, on the other hand, introduce a degree of centralization based on token holdings. Striking the right balance is crucial, and consensus algorithm evaluation aids in finding solutions that align with the desired level of decentralization.
Real-World Applications and Consensus Suitability
The choice of consensus algorithm greatly depends on the specific use case and application of the blockchain. Public blockchains might prioritize decentralization and security, while private or consortium blockchains may prioritize efficiency and scalability. Consensus algorithm evaluation tailors the choice to the unique requirements of the intended application.
Emerging Trends in Consensus Algorithms
The blockchain space is dynamic, and new consensus algorithms continue to emerge. Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), HoneyBadgerBFT, and Raft are examples of alternative consensus models gaining attention. Consensus algorithm evaluation involves staying abreast of these trends and assessing their applicability in different contexts.
Evaluating Trade-Offs for Optimal Performance
Consensus algorithm evaluation inherently involves evaluating trade-offs. Whether it’s the trade-off between security and scalability, energy efficiency and decentralization, or other considerations, blockchain architects must carefully weigh these factors. Evaluating trade-offs ensures that the selected consensus algorithm aligns with the overall goals and priorities of the blockchain network.
Consensus Algorithm Evaluation: Paving the Future of Blockchain
In summary, the landscape of consensus algorithm evaluation is central to the evolution of blockchain technology. Navigating the choices between PoW, PoS, and emerging models requires a nuanced understanding of their implications. As blockchain continues to mature, the ability to evaluate and adapt consensus algorithms will play a pivotal role in shaping the efficiency and sustainability of decentralized systems.
To delve deeper into the world of consensus algorithm evaluation and its impact on blockchain efficiency, explore Consensus Algorithm Evaluation.
In conclusion, the intricacies of consensus algorithms underscore the complexity of designing efficient and secure blockchain networks. As blockchain technology advances, consensus algorithm evaluation becomes an iterative and adaptive process, ensuring that the chosen model aligns with the evolving needs of the decentralized ecosystem.