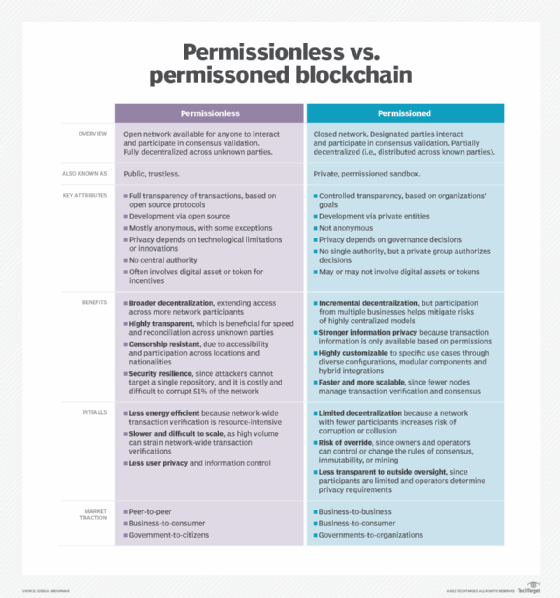
Innovative Design: Crafting Efficient Blockchain Protocols

Crafting the Future: Innovative Blockchain Protocol Design
Blockchain protocol design stands at the forefront of technological innovation, shaping the landscape of decentralized systems. In this exploration, we delve into the key aspects of designing efficient blockchain protocols and the impact they have on the broader blockchain ecosystem.
The Foundation: Understanding Blockchain Protocols
At the core of every blockchain lies its protocol – the set of rules and processes that govern the network. Blockchain protocols define how transactions are verified, added to the ledger, and how consensus is achieved among the network participants. A well-crafted protocol is essential for the reliability and security of a blockchain system.
Efficiency and Scalability Challenges
One of the primary considerations in blockchain protocol design is addressing the challenges of efficiency and scalability. As the popularity of blockchain networks grows, the demand for faster transaction processing and increased capacity becomes crucial. Innovations in consensus algorithms, such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS) or sharding, aim to enhance the efficiency and scalability of blockchain protocols.
Security Measures in Protocol Design
Security is paramount in blockchain systems, and protocol design plays a pivotal role in ensuring a robust defense against potential threats. Techniques like cryptographic hashing, digital signatures, and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) are integrated into protocols to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of data within the blockchain.
Interoperability: Bridging Blockchains
In a world with numerous blockchain networks, interoperability is a key consideration. Blockchain protocol design must enable seamless communication and data transfer between different blockchains. Initiatives like cross-chain communication protocols and interoperability standards contribute to a more interconnected and collaborative blockchain ecosystem.
Tokenomics and Economic Models
Beyond technical considerations, successful blockchain protocols often incorporate well-thought-out tokenomics and economic models. These elements incentivize network participants, promote decentralization, and contribute to the overall sustainability of the blockchain. Token design, distribution mechanisms, and governance structures all play a role in shaping the economic foundation of a blockchain protocol.
Accessibility and User Experience
User experience is a critical aspect of blockchain adoption. Protocol designers strive to create intuitive and user-friendly systems to encourage broader participation. Improving the onboarding process, reducing transaction fees, and enhancing overall accessibility contribute to making blockchain technology more user-centric.
Blockchain Protocol Design in Action
To witness the impact of innovative blockchain protocol design, explore Blockchain Protocol Design. This platform showcases real-world examples and case studies, providing insights into the diverse approaches taken by blockchain projects in crafting their protocols.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the Legal Landscape
As blockchain technology evolves, so do regulatory considerations. Protocol designers must navigate the complex legal landscape to ensure compliance with local and international regulations. Striking a balance between decentralization and adherence to legal standards is crucial for the long-term success of blockchain projects.
Ethical Considerations in Design Choices
Blockchain protocol designers also face ethical considerations in their design choices. Issues such as environmental impact, data privacy, and social responsibility come to the forefront. Ethical design practices ensure that blockchain protocols align with broader societal values and contribute positively to the communities they serve.
The Future of Blockchain Protocol Design
The journey of blockchain protocol design is an ongoing exploration, with continuous innovation and adaptation to emerging challenges. The future holds exciting possibilities as designers push the boundaries of efficiency, security, and user experience. The collaborative effort of the blockchain community will undoubtedly shape the next generation of decentralized systems.
In conclusion, the innovative design of blockchain protocols is a dynamic process that involves addressing technical challenges, enhancing security, promoting economic sustainability, and considering ethical implications. The evolution of blockchain protocol design is instrumental in realizing the full potential of decentralized technologies, paving the way for a more inclusive and efficient digital future.