Layer 2 Scaling: Elevating Blockchain Efficiency

Elevating Blockchain Efficiency: A Dive into Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 scaling solutions have emerged as a game-changer in the blockchain space, addressing scalability issues and enhancing the efficiency of blockchain networks. In this exploration, we delve into the world of Layer 2 scaling, understanding its significance and impact on the broader blockchain ecosystem.
The Scalability Challenge in Blockchain
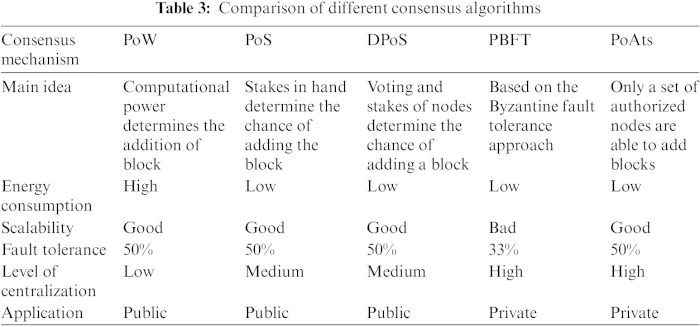
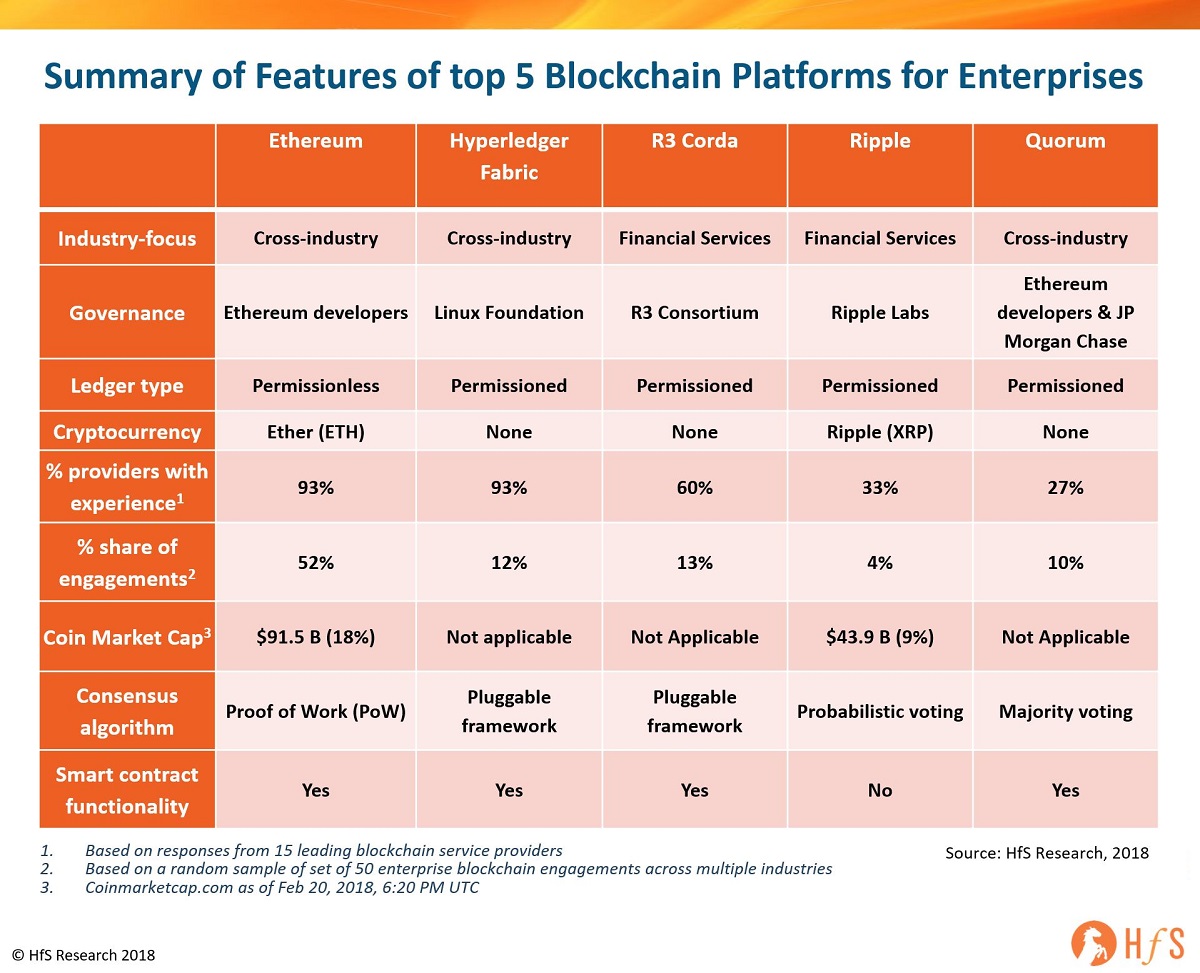
Scalability has long been a concern for blockchain networks, particularly as they gain popularity and user adoption increases. The traditional consensus mechanisms, while providing security, often face limitations in terms of transaction throughput and confirmation times. Layer 2 scaling solutions aim to overcome these challenges by building on top of existing blockchains.
Understanding Layer 2 Scaling
Layer 2 scaling refers to solutions that operate on a layer above the base blockchain layer. Instead of processing every transaction directly on the main chain, Layer 2 solutions facilitate off-chain processes or sidechains, reducing the burden on the main blockchain. This approach enhances scalability without compromising the security and decentralization principles of the underlying blockchain.
Types of Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
There are various types of Layer 2 scaling solutions, each with its unique approach to improving scalability. Two prominent categories include sidechains, which are independent blockchains connected to the main chain, and state channels, which enable off-chain transactions between participants. These solutions offer flexibility and cater to different use cases within the blockchain ecosystem.
Sidechains: Parallel Universes for Scalability
Sidechains provide an additional layer of scalability by creating independent blockchains connected to the main blockchain. Transactions that do not require immediate confirmation on the main chain can be processed on the sidechain, alleviating congestion and speeding up overall transaction processing. This parallel approach significantly increases the network’s capacity.
State Channels: Off-chain Transaction Magic
State channels enable off-chain transactions between participants, allowing them to interact directly without involving the main blockchain for every step. This minimizes the need for on-chain transactions, reducing congestion and fees. State channels are particularly useful for scenarios where frequent interactions occur between specific users, such as gaming or micropayments.
Real-world Implementation: Layer 2 Scaling Solutions in Action
To witness the impact of Layer 2 scaling solutions firsthand, explore Layer 2 Scaling Solutions. This platform offers insights into real-world examples and case studies, showcasing the practical application and benefits of integrating Layer 2 solutions into blockchain networks.
Benefits of Layer 2 Scaling
Layer 2 scaling solutions bring a host of benefits to blockchain networks. Apart from improved scalability, they contribute to faster transaction confirmation times, reduced fees, and enhanced user experience. These advantages make blockchain technology more accessible and practical for a broader range of applications.
Overcoming Challenges and Trade-offs
While Layer 2 scaling solutions offer substantial advantages, they are not without challenges and trade-offs. Issues such as interoperability, security considerations, and the need for user adoption pose ongoing challenges. Striking a balance between scalability and maintaining the integrity of the underlying blockchain requires continuous innovation and development.
The Future of Blockchain Scalability
As blockchain technology evolves, Layer 2 scaling solutions are likely to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of blockchain scalability. The combination of Layer 2 solutions with other advancements, such as improved consensus mechanisms and cross-chain interoperability, holds the promise of creating a more scalable, efficient, and interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
Conclusion: Scaling New Heights
In conclusion, Layer 2 scaling solutions mark a significant milestone in addressing the scalability challenges of blockchain networks. By elevating efficiency through sidechains, state channels, and other innovative approaches, these solutions contribute to a more scalable and user-friendly blockchain experience. As the industry continues to explore and implement Layer 2 scaling, the potential for mainstream adoption and diverse use cases in blockchain technology grows.