Cross-Platform DApp Development Strategies for Success

Cross-Platform DApp Development Strategies for Success
In the ever-evolving landscape of decentralized applications (DApps), developers face the challenge of ensuring compatibility across multiple platforms. Effective cross-platform DApp development is essential for reaching a broader audience and providing a seamless user experience. Let’s explore key strategies to enhance the success of your cross-platform DApp development endeavors.
Understanding Cross-Platform Challenges
Developers encounter various challenges when aiming to create DApps that work seamlessly across different platforms. These challenges include differences in operating systems, device specifications, and browser compatibility. Addressing these issues is crucial for delivering a consistent user experience.
Adopting Cross-Platform Frameworks
To overcome the challenges of diverse platforms, developers often turn to cross-platform frameworks. These frameworks allow for the creation of applications that can run on multiple platforms without significant code modifications. Examples include React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin. Choosing the right framework can streamline development and ensure a wider reach for your DApp.
Ensuring User-Friendly Interfaces
A critical aspect of successful cross-platform DApp development is designing user interfaces that adapt well to various screen sizes and resolutions. Responsive design principles play a vital role in ensuring that users have a consistent and intuitive experience, regardless of the device they are using.
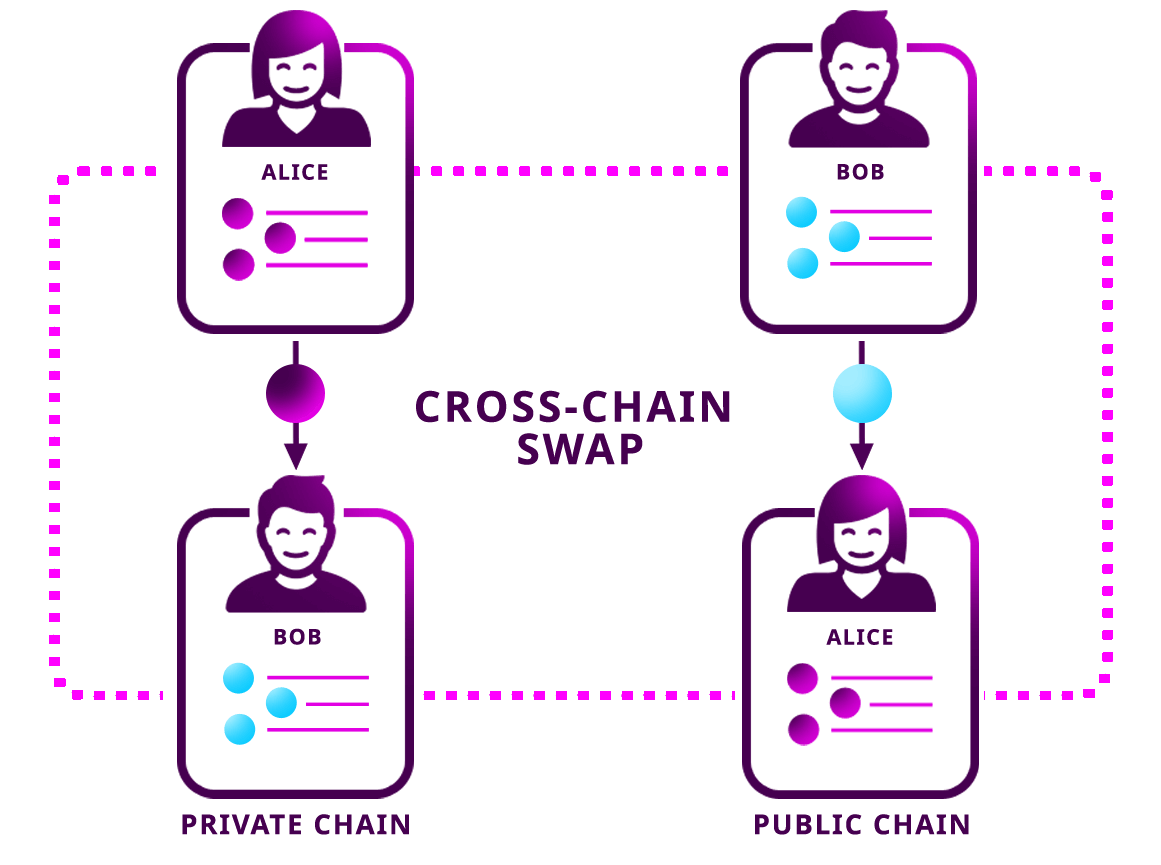
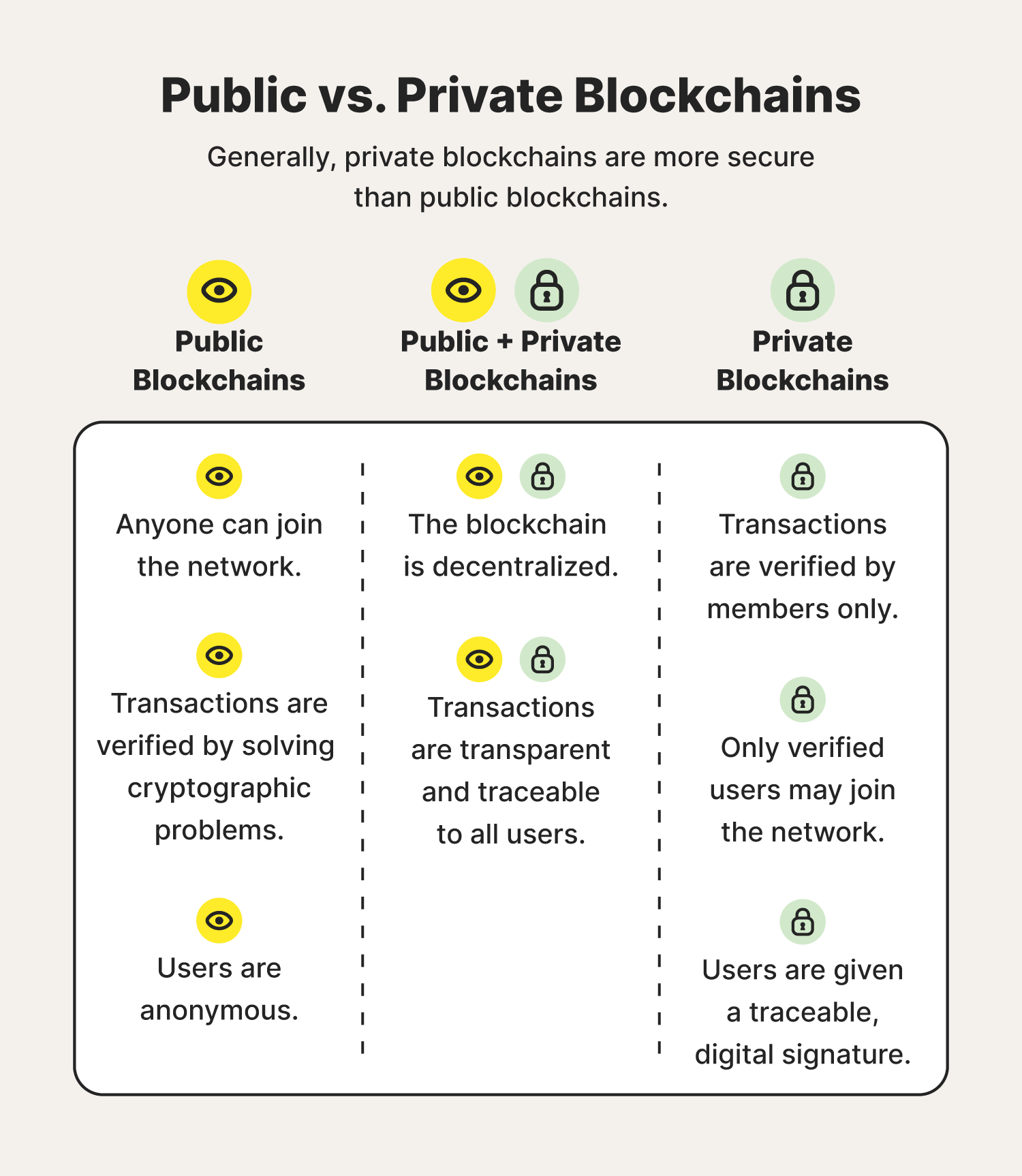
Implementing Cross-Chain Compatibility
In the blockchain space, interoperability between different chains is essential for fostering a connected ecosystem. Developing DApps that can seamlessly interact with various blockchains enhances their utility and opens up new possibilities. Cross-Chain Development is an integral part of building versatile and widely adopted DApps.
Testing Across Multiple Environments
Thorough testing is paramount in cross-platform DApp development. Rigorous testing across various environments helps identify and address compatibility issues early in the development process. This includes testing on different devices, browsers, and operating systems to ensure a smooth user experience for all.
Leveraging Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based solutions can significantly simplify cross-platform DApp development. Utilizing cloud services for backend infrastructure and data storage ensures that your DApp can function seamlessly across different platforms without compromising on performance or security.
Embracing Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
Progressive Web Apps offer a compelling solution for cross-platform compatibility. By combining the best of web and mobile applications, PWAs provide users with an app-like experience directly from their browsers. This approach minimizes the need for platform-specific development and ensures a consistent experience across devices.
Optimizing for Cross-Platform Performance
Ensuring optimal performance on diverse platforms is crucial for user satisfaction. Employing performance optimization techniques, such as code splitting, lazy loading, and image optimization, can significantly enhance the speed and responsiveness of your cross-platform DApp.
Continuous Updates and Maintenance
The digital landscape is dynamic, with constant updates to operating systems, browsers, and frameworks. To maintain cross-platform compatibility, developers must stay vigilant and update their DApps accordingly. Regular maintenance ensures that your DApp remains functional and secure across evolving platforms.
In conclusion, successful cross-platform DApp development requires a combination of thoughtful design, strategic framework selection, and diligent testing. By embracing interoperability, optimizing performance, and staying abreast of technological advancements, developers can create DApps that thrive across a multitude of platforms. Explore the vast potential of Cross-Platform DApp Development to unlock new opportunities in the decentralized future.
Learn more about Cross-Platform DApp Development and take your DApp projects to new heights.