Navigating Consensus: Unraveling Blockchain Mechanisms

Navigating Consensus: Unraveling Blockchain Mechanisms
In the realm of blockchain technology, consensus mechanisms form the backbone of secure and decentralized networks. This article delves into the intricacies of various blockchain consensus mechanisms, highlighting their importance in ensuring trust, security, and reliability within distributed ledgers.
Understanding Consensus Mechanisms: The Pillars of Blockchain Security
Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure all nodes in a blockchain network agree on the state of the ledger. They play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and security of the decentralized system by preventing malicious actors from manipulating transactions. Different consensus mechanisms employ distinct algorithms, each with its strengths and suitability for specific blockchain applications.
Proof of Work (PoW): The Pioneer of Consensus
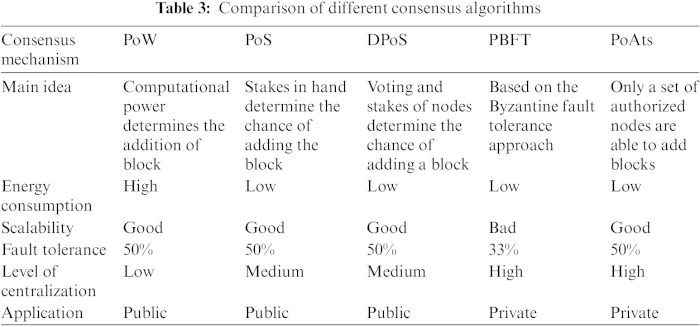
Proof of Work is the original consensus mechanism, famously associated with Bitcoin. In PoW, participants, known as miners, solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This energy-intensive process secures the network by making it computationally expensive to perform malicious activities. While effective, PoW has faced criticism due to its environmental impact and scalability challenges.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Shifting the Paradigm
In contrast to PoW, Proof of Stake selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This approach reduces the need for energy-intensive computations, making PoS more environmentally friendly. Ethereum’s planned transition to Ethereum 2.0, which involves a shift from PoW to PoS, highlights the increasing popularity of this consensus mechanism.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Enhancing Efficiency
Delegated Proof of Stake introduces a more democratic element to the consensus process. Token holders vote for a limited number of delegates who are responsible for validating transactions and producing blocks. DPoS aims to improve scalability and efficiency, as a smaller group of trusted entities facilitates the consensus process. Platforms like EOS and Tron utilize DPoS to enhance their blockchain networks.
Proof of Authority (PoA): Prioritizing Identity and Trust
In Proof of Authority, validators are chosen based on their identity and reputation rather than their stake or computational power. This approach prioritizes trust and reliability, making PoA suitable for private or consortium blockchains where participants are known entities. It reduces the risk of malicious actors and enhances the network’s stability.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): Ensuring Agreement
PBFT is a consensus mechanism designed to tolerate Byzantine faults, meaning it can maintain consensus even if some nodes in the network are malicious. It operates through a series of rounds where nodes exchange messages to achieve agreement on the state of the ledger. PBFT is often employed in permissioned blockchain networks where participants are known and trusted.
Hybrid Consensus Mechanisms: Balancing Trade-Offs
Some blockchain networks utilize hybrid consensus mechanisms that combine elements of different approaches. For example, a blockchain may employ a PoW mechanism for initial block creation and then transition to a PoS system for ongoing block validation. These hybrid models aim to capitalize on the strengths of multiple mechanisms while mitigating their individual weaknesses.
The Importance of Consensus in Blockchain Applications: Trust and Security
Consensus mechanisms are fundamental to the success of blockchain applications. They ensure that all participants in the network reach an agreement on the validity of transactions, fostering trust in the system. The robustness of the chosen consensus mechanism directly impacts the security, scalability, and efficiency of the blockchain, making it a critical consideration for developers and stakeholders.
Evolving Landscape: Continuous Innovation in Consensus
As the blockchain space evolves, researchers and developers continue to explore and innovate in the realm of consensus mechanisms. New approaches, such as Proof of Space, Proof of Burn, and Proof of History, are being explored to address the limitations and challenges posed by existing consensus models. This continuous innovation aims to create more sustainable, secure, and scalable blockchain networks.
Conclusion: The Tapestry of Trust in Blockchain
In conclusion, blockchain consensus mechanisms weave the tapestry of trust that underpins decentralized networks. From the pioneering Proof of Work to the evolving landscape of innovative approaches, each consensus mechanism contributes to the reliability and security of blockchain applications. To explore more about Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com.