Securing Harmony: Consensus Algorithm’s Vital Security

Securing Harmony: Navigating Consensus Algorithm Security
Consensus algorithms form the backbone of blockchain networks, ensuring agreement among participants. This article delves into the crucial aspect of consensus algorithm security, exploring its significance, challenges, and the measures in place to safeguard the integrity and reliability of decentralized systems.
Understanding Consensus Algorithms
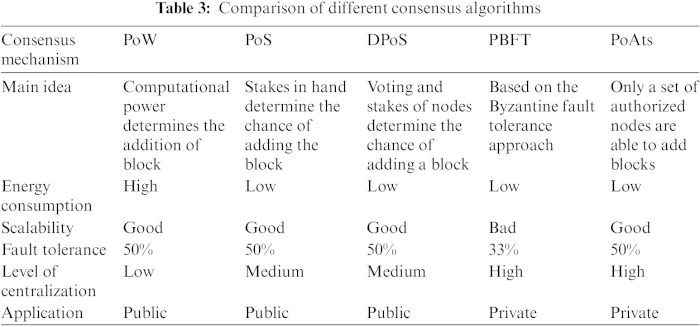
Consensus algorithms enable distributed systems to reach agreement on the state of a shared ledger. They play a pivotal role in maintaining the trust and integrity of blockchain networks. Common consensus algorithms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), each with its own approach to achieving consensus.
The Significance of Security in Consensus
Security is paramount in consensus algorithms, as any compromise can lead to severe consequences, including double-spending, unauthorized modifications to the ledger, and network instability. A secure consensus algorithm ensures that the majority of network participants are honest, preventing malicious actors from manipulating the system.
Proof of Work (PoW) Security Considerations
Proof of Work, the algorithm behind Bitcoin’s consensus, relies on miners solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. PoW’s security is based on the computational effort required to solve these puzzles. However, concerns include the potential for 51% attacks, where an entity controls the majority of the network’s mining power, compromising consensus.
Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) Security Mechanisms
Proof of Stake and its variant, Delegated Proof of Stake, address PoW’s energy inefficiency by relying on participants’ ownership or delegation of cryptocurrency. While considered more eco-friendly, their security mechanisms hinge on participants having a vested interest in maintaining the integrity of the network. Challenges include the “nothing at stake” problem and potential centralization risks in DPoS.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) for Fast and Secure Consensus
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance aims for fast consensus in a permissioned setting. Participants reach agreement as long as a two-thirds majority is honest. PBFT ensures security against malicious nodes but is designed for a trusted environment, making it less suitable for fully decentralized and open blockchain networks.
Security Threats and Challenges in Consensus Algorithms
Consensus algorithm security faces various threats, including the risk of centralization, the potential for collusion among participants, and susceptibility to novel attack vectors. Addressing these challenges requires continuous research, vigilance, and the development of resilient consensus mechanisms that can adapt to evolving threats.
Innovations and Enhancements in Consensus Security
Ongoing research and development aim to enhance consensus algorithm security. Innovations include hybrid consensus models, combining the strengths of different algorithms, and the exploration of novel approaches such as Proof of Space, Proof of Burn, and Proof of Authority. These endeavors seek to mitigate existing challenges and ensure the long-term security of blockchain networks.
Consensus Algorithm Security Best Practices
To fortify consensus algorithm security, adhering to best practices is essential. Regular audits, code reviews, and continuous monitoring help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Additionally, promoting a diverse and decentralized network of participants contributes to a more robust security posture.
The Role of Community and Governance in Consensus Security
Community involvement and governance mechanisms are vital in ensuring consensus algorithm security. Transparent decision-making processes, active community engagement, and mechanisms for resolving disputes contribute to the overall resilience of the consensus algorithm.
Consensus Algorithm Security at fireboyandwatergirlplay.com
For in-depth insights into consensus algorithm security and access to valuable resources, visit Consensus Algorithm Security. This platform serves as a hub for knowledge, discussions, and updates, offering a comprehensive view of the evolving landscape of consensus algorithm security in blockchain networks.
Conclusion: Safeguarding the Foundation of Trust
In conclusion, consensus algorithm security is foundational to the trust and reliability of blockchain networks. As these networks continue to evolve, the security of consensus mechanisms becomes even more critical. By understanding the significance, addressing challenges, implementing best practices, and staying informed through dedicated platforms, we can collectively contribute to safeguarding the foundation of trust in decentralized systems.