Demystifying 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657

Unveiling the Power of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
Understanding the Basics of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
In the fast-paced world of cryptocurrencies, understanding the fundamentals of innovative platforms like 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 is crucial. At its core, 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 represents a groundbreaking technology that promises to revolutionize various aspects of the digital economy.
Exploring the Technology Behind 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
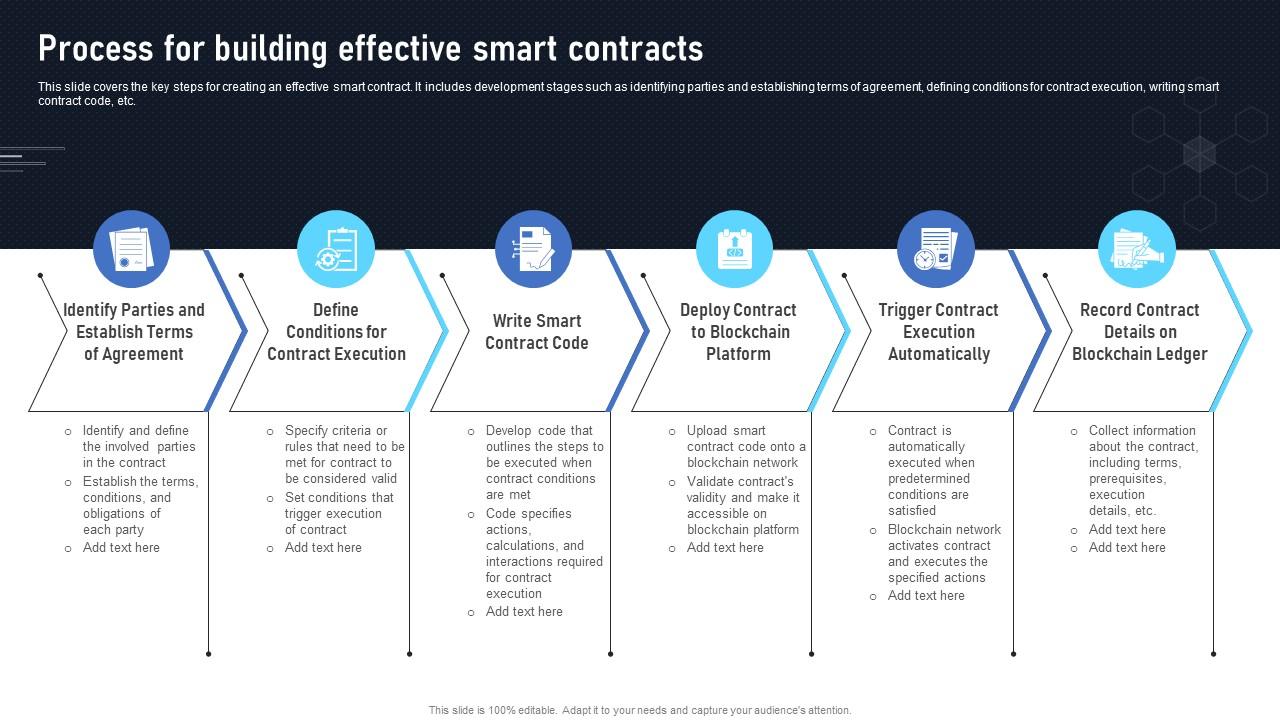
The technology powering 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 is decentralized and built on the principles of blockchain. This decentralized architecture ensures transparency, security, and immutability, making it an ideal platform for conducting digital transactions.
Unlocking the Potential Applications of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
One of the most intriguing aspects of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 is its versatility. From decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), the platform opens up a myriad of possibilities for developers and users alike. Its ability to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries makes it a game-changer in various industries.
Navigating the Advantages of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
The advantages offered by 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 are numerous. Its decentralized nature ensures that users have full control over their digital assets, eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries. Moreover, its open and permissionless architecture promotes innovation and fosters a vibrant ecosystem of developers and users.
Exploring the Future Possibilities of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
As the digital economy continues to evolve, the future possibilities of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 are limitless. From disrupting traditional finance to revolutionizing supply chain management, the platform has the potential to reshape entire industries. With ongoing research and development, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases emerge in the years to come.
Innovating with 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
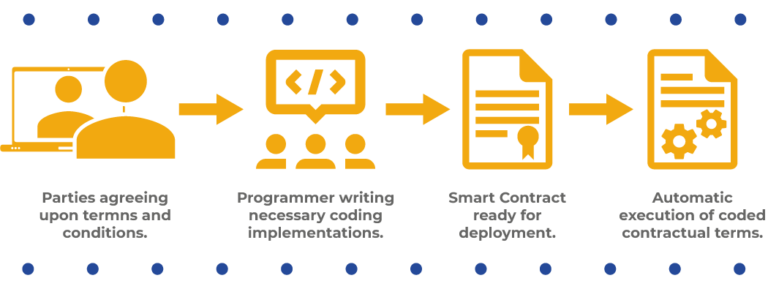
Innovation is at the core of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657. Its decentralized architecture and smart contract functionality enable developers to create innovative solutions that were previously unimaginable. Whether it’s creating decentralized exchanges or tokenizing real-world assets, the platform empowers developers to push the boundaries of what’s possible in the digital space.
Deciphering the Challenges of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 Adoption
While the potential of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 is undeniable, adoption remains a challenge. As with any emerging technology, there are hurdles to overcome, including scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and user experience. However, with ongoing development and collaboration within the crypto community, these challenges can be addressed to realize the full potential of the platform.
Embracing the Future with 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657
In conclusion, 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 represents a paradigm shift in the world of cryptocurrencies. Its decentralized architecture, innovative features, and potential applications make it a force to be reckoned with in the digital economy. By understanding its basics, exploring its technology, and embracing its future possibilities, we can unlock the full power of 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657 and shape the future of finance together. Read more about 0x3e9a8df87b2126393e5b492e2aec3146eb8c6657