Automating Agreements: Smart Contract Execution Mastery
Automating Agreements: Smart Contract Execution Mastery
Smart contracts have revolutionized the way agreements are executed in the digital realm, bringing efficiency, transparency, and automation to contractual processes. This article delves into the intricacies of smart contract execution, exploring its key features, benefits, and real-world applications.
Understanding Smart Contract Execution
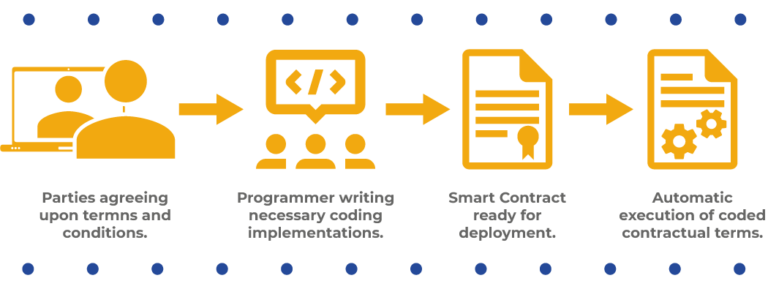
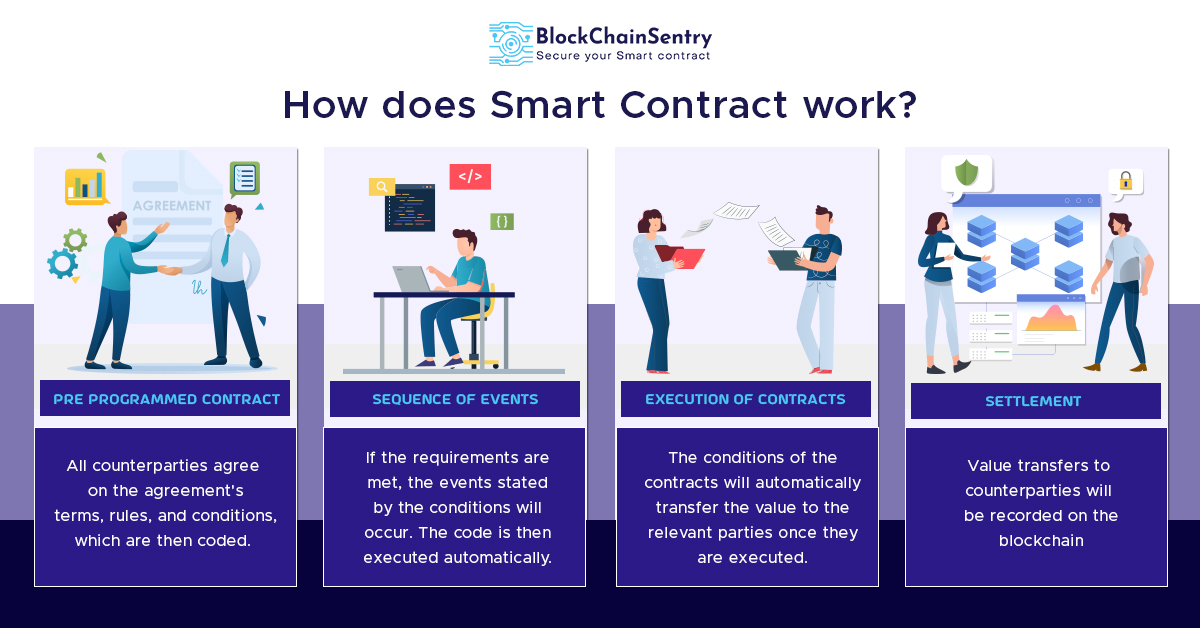
Smart contract execution is the process by which a self-executing contract, encoded with predefined rules and conditions, automatically enforces and executes contractual clauses without the need for intermediaries. This process occurs on a blockchain, providing security, immutability, and transparency to the entire execution journey.
Key Features of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts possess several key features that set them apart. They are tamper-proof, ensuring that once deployed on the blockchain, their code cannot be altered. They are self-executing, meaning they automatically enforce contractual terms when predefined conditions are met. Additionally, smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of errors and delays in the execution process.
Automation and Efficiency
The primary advantage of smart contract execution lies in its automation capabilities. Traditional contract execution involves manual intervention, verification, and enforcement. Smart contracts automate these steps, reducing the time and resources required for the execution of agreements. This automation streamlines processes and minimizes the potential for human error.
Transparency and Immutability
Smart contract execution occurs on a decentralized and transparent blockchain. Every step of the contract’s lifecycle, from creation to execution, is recorded and visible to all relevant parties. This transparency enhances trust among participants, as the terms and conditions are verifiable and immutable once deployed on the blockchain.
Real-World Applications of Smart Contract Execution
Smart contract execution finds applications across various industries. In finance, smart contracts automate processes such as lending, borrowing, and trading on decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. Supply chain management utilizes smart contracts to enhance transparency and traceability. Real estate transactions benefit from automated and secure contract execution, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Challenges and Considerations
While smart contract execution offers significant advantages, challenges exist. The “oracle problem,” which involves integrating real-world data into smart contracts, poses a hurdle. Ensuring the security of the underlying code is crucial to prevent vulnerabilities and exploits. Additionally, legal recognition and regulatory frameworks for smart contracts are areas that need further development.
Smart Contract Execution in Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Decentralized applications, or DApps, leverage smart contract execution to automate various functions. DApps in gaming, finance, and governance utilize smart contracts to facilitate interactions and transactions among users. The programmable nature of smart contracts allows DApp developers to create innovative and decentralized solutions.
The Future of Smart Contract Execution
The future of smart contract execution holds exciting possibilities. Ongoing research and development aim to address current challenges and enhance the capabilities of smart contracts. Integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the evolution of interoperability standards contribute to the continuous advancement of smart contract execution.
Security Best Practices
Ensuring the security of smart contracts is paramount. Best practices include thorough code audits, utilizing established standards like ERC-20 for token contracts, and implementing multi-signature wallets for added security. Smart contract developers must stay vigilant to emerging threats and continuously update code to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Smart Contract Execution – Learn More
To delve deeper into Smart Contract Execution, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com. This comprehensive resource offers additional insights, tutorials, and updates on the latest developments in the world of smart contracts and their mastery in automating digital agreements.
In conclusion, smart contract execution represents a pivotal shift in how agreements are made and enforced in the digital age. Its automation, transparency, and efficiency reshape traditional contractual processes across industries. As the technology continues to mature, smart contract execution is poised to play a central role in the evolution of decentralized and automated ecosystems.