Efficient Cross-Border Payments: Innovative Solutions for Global Transactions

Navigating the Landscape of Cross-Border Payment Solutions
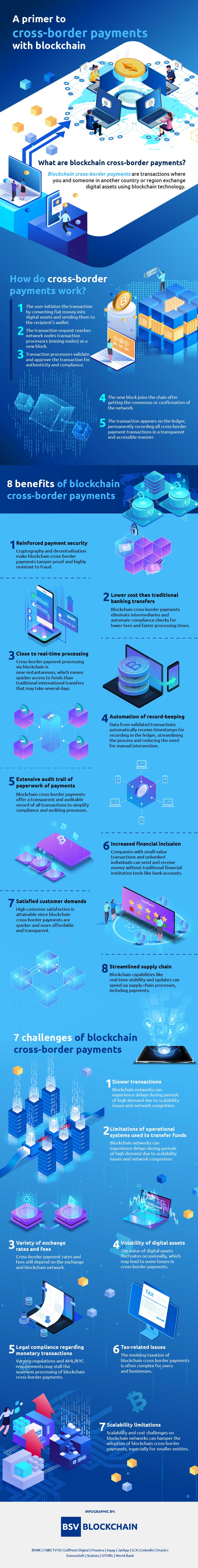
In our interconnected global economy, the need for efficient and reliable cross-border payment solutions has never been more critical. Businesses and individuals alike seek methods that streamline transactions across borders, mitigating challenges associated with traditional banking systems.
Challenges in Traditional Cross-Border Payments
Traditional cross-border payment processes often involve multiple intermediaries, leading to delays, high fees, and a lack of transparency. The inefficiencies in legacy systems create obstacles for businesses aiming to expand globally and for individuals managing international transactions.
The Rise of Innovative Cross-Border Payment Solutions
In response to the limitations of traditional methods, innovative cross-border payment solutions have emerged, leveraging advancements in technology to offer faster, more cost-effective, and transparent alternatives. These solutions aim to revolutionize the way we transfer value across borders.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Solutions
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and transparent nature, has paved the way for cryptocurrency-based cross-border payment solutions. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and stablecoins are increasingly being utilized for their ability to facilitate near-instantaneous transactions with reduced fees, overcoming the limitations of traditional banking systems.
Fintech Platforms Driving Efficiency
Fintech platforms play a pivotal role in the evolution of cross-border payment solutions. These platforms leverage cutting-edge technologies, data analytics, and mobile accessibility to provide users with seamless and user-friendly international payment options. Fintech disruptors are reshaping the landscape by offering alternatives that are agile, cost-effective, and tailored to modern expectations.
Mobile Wallets and Digital Payment Apps
The ubiquity of smartphones has given rise to mobile wallet solutions and digital payment apps that enable cross-border transactions at the fingertips of users. These solutions offer convenience, speed, and often integrate features like real-time currency conversion, further enhancing the user experience for international transactions.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
As cross-border payment solutions evolve, navigating regulatory landscapes becomes crucial. Compliance with international financial regulations and anti-money laundering (AML) standards is essential for ensuring the legitimacy and security of transactions. Innovators in the space actively collaborate with regulators to establish frameworks that foster both innovation and accountability.
The Role of Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges serve as crucial intermediaries for those utilizing digital assets for cross-border payments. These platforms provide liquidity, facilitate currency conversions, and ensure the seamless transfer of value across borders. The integration of cryptocurrencies into mainstream finance is reshaping cross-border payment ecosystems.
Cross-Border Payment Solutions for Businesses
Businesses engaged in international trade require specialized cross-border payment solutions tailored to their unique needs. Platforms offering features like multi-currency accounts, automated reconciliation, and risk management tools empower businesses to navigate the complexities of global transactions more efficiently.
Looking Ahead: A Global Payment Revolution
The ongoing evolution of cross-border payment solutions signals a global payment revolution. As technology continues to advance and user expectations evolve, the financial industry is witnessing a shift towards solutions that prioritize speed, cost-efficiency, and accessibility. The future promises a more connected world where cross-border transactions are seamless and inclusive.
To explore the diverse landscape of cross-border payment solutions and their impact on global transactions, visit Cross-Border Payment Solutions.
In conclusion, the landscape of cross-border payments is undergoing a transformative shift driven by technological innovation. From blockchain-powered solutions to fintech platforms and mobile wallets, the options available for efficient and seamless international transactions are expanding. As businesses and individuals embrace these advancements, the global financial ecosystem is poised for a new era of connectivity and convenience.