Fortifying Chains: Essential Blockchain Security Measures
Guardians of Trust: Navigating Essential Blockchain Security Measures
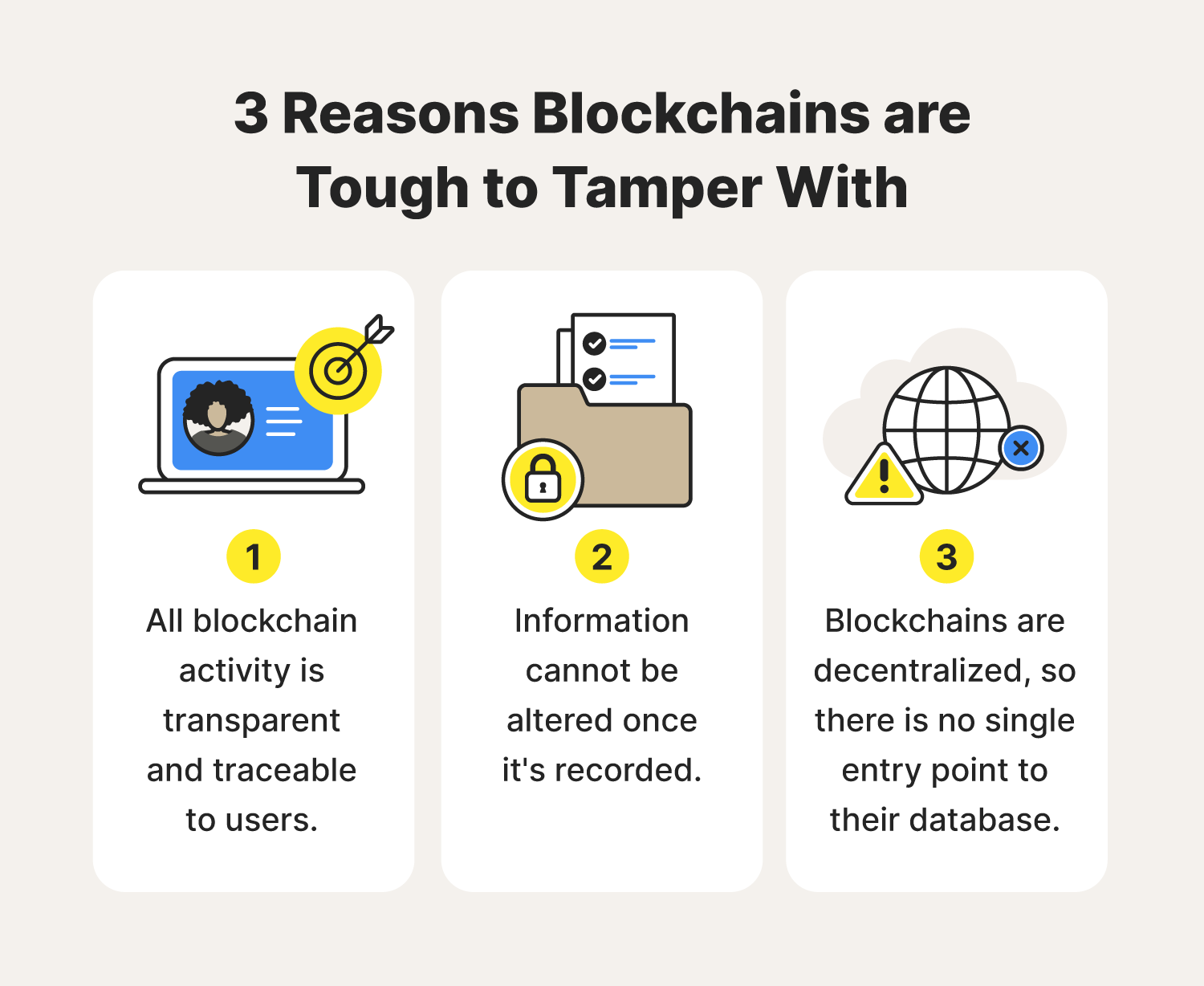
Blockchain technology, hailed for its decentralization and transparency, requires robust security measures to safeguard against potential threats. This article explores the vital security measures that fortify the integrity of blockchain networks, ensuring the trust and reliability that the technology promises.
Cryptography: The Bedrock of Security
At the heart of blockchain security lies cryptography, the art of secure communication. Blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, control the creation of new units, and authenticate the transfer of assets. Public and private key pairs, hash functions, and digital signatures are integral components that form the foundation of a secure blockchain ecosystem.
Consensus Mechanisms: Unifying Trust
Consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of blockchain networks. By ensuring agreement on the state of the ledger among participants, consensus mechanisms eliminate the risk of fraudulent transactions. Popular mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) contribute to the overall security and trustworthiness of the blockchain.
Smart Contract Audits: Code Assurance
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with predefined rules, are susceptible to vulnerabilities. Conducting thorough smart contract audits is a fundamental security measure. Audits involve a comprehensive review of the contract’s code, logic, and potential vulnerabilities. By identifying and rectifying issues before deployment, smart contract audits enhance the reliability and security of decentralized applications (DApps).
Network Security: Shielding Against External Threats
Blockchain networks are not immune to external threats, and network security measures are essential to prevent attacks. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, Sybil attacks, and 51% attacks are potential threats that can compromise the network’s functionality. Implementing robust network security measures helps mitigate these risks and ensures the continuous and secure operation of the blockchain.
Permissioned Blockchains: Controlled Access
While public blockchains are open and decentralized, permissioned blockchains restrict access to a predetermined group of participants. This controlled access enhances security by reducing the attack surface and preventing unauthorized entities from participating in the network. Permissioned blockchains are often favored in enterprise settings where privacy and regulatory compliance are paramount.
Cold and Multi-Signature Wallets: Safeguarding Assets
Securing cryptocurrency assets is a critical aspect of blockchain security. Cold wallets, which are not connected to the internet, provide an additional layer of protection against hacking attempts. Multi-signature wallets, requiring multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, enhance security by distributing control among multiple parties, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Regular Software Updates: Staying Ahead of Threats
Blockchain protocols and software evolve over time, and staying up-to-date with the latest releases is essential for security. Regular software updates often include patches for identified vulnerabilities and enhancements to overall system security. By promptly applying updates, blockchain networks can stay ahead of potential threats and ensure a resilient security posture.
Education and Training: Empowering Users
Security is not solely a technological consideration; user awareness is equally crucial. Education and training programs empower users to understand and implement best practices for securing their digital assets and participating in blockchain networks securely. Increased awareness fosters a community that actively contributes to the overall security of the blockchain ecosystem.
Incident Response Plans: Preparedness for the Unexpected
Despite preventive measures, the possibility of security incidents cannot be entirely ruled out. Establishing robust incident response plans is a proactive approach to handle unforeseen security events. These plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, minimizing the impact and facilitating a swift and coordinated response.
Blockchain Security Measures at fireboyandwatergirlplay.com
For a comprehensive exploration of essential blockchain security measures and insights into best practices, visit Blockchain Security Measures. This platform serves as a valuable resource, offering guidance and updates to fortify the security of blockchain networks and instill confidence in users and stakeholders.
Conclusion: A Secure Foundation for Decentralization
In conclusion, the strength of blockchain technology lies not only in its decentralization but also in the robust security measures that uphold trust and integrity. From cryptographic foundations to incident response preparedness, each security measure plays a crucial role in fortifying the resilience of blockchain networks. As the technology continues to evolve, the emphasis on security measures remains paramount, ensuring a secure foundation for the decentralized future.






