Empowering Transactions: The Art of Smart Contract Deployment

Empowering Transactions: The Art of Smart Contract Deployment
Smart contracts, a cornerstone of blockchain technology, have revolutionized the way transactions are executed and automated. In this exploration, we delve into the intricate process of smart contract deployment, unraveling the nuances that empower transactions and redefine trust in decentralized systems.
Understanding Smart Contracts: A Digital Agreement Revolution
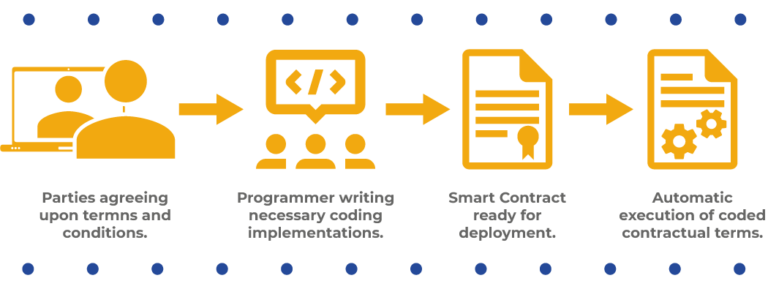
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with coded terms directly written into lines of code. They run on blockchain platforms and automatically execute predefined actions when specified conditions are met. Essentially, these digital agreements facilitate and enforce contractual agreements without the need for intermediaries, providing a trustless and transparent mechanism for transactions.
Coding the Terms: The Heart of Smart Contract Deployment
Smart contract deployment begins with the coding of terms. Developers meticulously define the conditions, actions, and participants’ roles within the contract. This coding phase requires precision and attention to detail, ensuring that the smart contract operates seamlessly and as intended. Common programming languages, such as Solidity for Ethereum, are often employed in this crucial phase.
Choosing the Blockchain Platform: Where the Contract Resides
Selecting the appropriate blockchain platform is a pivotal decision in the smart contract deployment process. Different platforms offer distinct features, consensus mechanisms, and capabilities. Ethereum, with its robust smart contract functionality, remains a popular choice, while other platforms like Binance Smart Chain and Polkadot provide alternative environments for deployment, each with its unique advantages.
Testing for Perfection: Ensuring Flawless Execution
Before deploying a smart contract on the chosen blockchain, thorough testing is imperative. Developers engage in comprehensive testing to identify and eliminate any potential vulnerabilities or bugs. This meticulous process ensures that the smart contract operates flawlessly and that it can withstand the complexities of real-world transactions without compromising security or functionality.
Deployment on the Blockchain: Making the Contract Live
Once the smart contract has undergone rigorous testing, it’s ready for deployment on the chosen blockchain. The deployment process involves submitting the contract to the network, where it becomes live and accessible to users. This step requires a nominal fee known as gas, which compensates miners for validating and executing the contract on the blockchain.
Execution and Automation: Trust in Code
Smart contracts operate autonomously once deployed, executing actions when predefined conditions are met. This automation eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of errors and fraud. Participants can trust that the terms of the contract will be executed faithfully, as the code governs the process transparently and impartially.
Interacting with Smart Contracts: User Engagement
Users interact with smart contracts through transactions on the blockchain. Whether it’s a payment, a token swap, or any other action specified in the contract, participants engage with the smart contract by submitting transactions to the blockchain. This interaction is seamless and occurs in a trustless environment, as the smart contract ensures the proper execution of the agreed-upon terms.
Evolving Standards: ERC-20, ERC-721, and Beyond
Smart contract deployment has given rise to standards that define the functionality and features of contracts within the blockchain ecosystem. Standards like ERC-20 for fungible tokens and ERC-721 for non-fungible tokens provide a common framework, fostering interoperability and enhancing the usability of smart contracts across various applications.
Challenges and Innovations: Navigating the Landscape
While smart contracts have brought about transformative changes, challenges persist. Security vulnerabilities, scalability concerns, and interoperability issues are areas of ongoing focus. Innovations such as layer-two solutions, cross-chain interoperability, and improved programming languages aim to address these challenges, pushing the boundaries of what smart contracts can achieve.
Future Horizons: Smart Contracts in Tomorrow’s World
The landscape of smart contract deployment is dynamic, with continuous advancements shaping the future. As blockchain technology evolves, smart contracts are expected to play a pivotal role in industries beyond finance, including supply chain, healthcare, and governance. Their ability to automate and secure transactions positions smart contracts as a cornerstone of the decentralized future.
In conclusion, smart contract deployment is an intricate process that empowers transactions and revolutionizes the way agreements are executed in the digital realm. To explore more about Smart Contract Deployment, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com.