Navigating Blockchain Governance: Frameworks for Success
Navigating Blockchain Governance: Frameworks for Success
Blockchain, with its decentralized and transparent nature, requires effective governance frameworks to ensure its integrity and sustainability. Let’s explore the essential components and principles of blockchain governance frameworks, understanding their significance in the ever-evolving landscape.
Decentralization and Governance: The Core Challenge
At the heart of blockchain governance is the delicate balance between decentralization and effective decision-making. The decentralized nature of blockchain is a foundational principle, but effective governance is essential to address issues, implement upgrades, and respond to the evolving needs of the community. Striking this balance is a core challenge for blockchain projects.
Consensus Mechanisms and Decision-Making: Key Components
Consensus mechanisms are pivotal in blockchain governance, serving as the foundation for decision-making processes. Whether Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (PoS), or Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), the chosen consensus mechanism influences how decisions are reached. Governance frameworks define how stakeholders participate in decision-making, emphasizing inclusivity and fairness.
Participation and Stakeholder Involvement: Inclusive Governance Models
In successful blockchain governance, active participation and involvement of stakeholders are crucial. Governance frameworks should encourage transparency and inclusivity, allowing token holders, developers, miners, and other community members to contribute to decision-making processes. This ensures a diverse range of perspectives, promoting a more robust and resilient ecosystem.
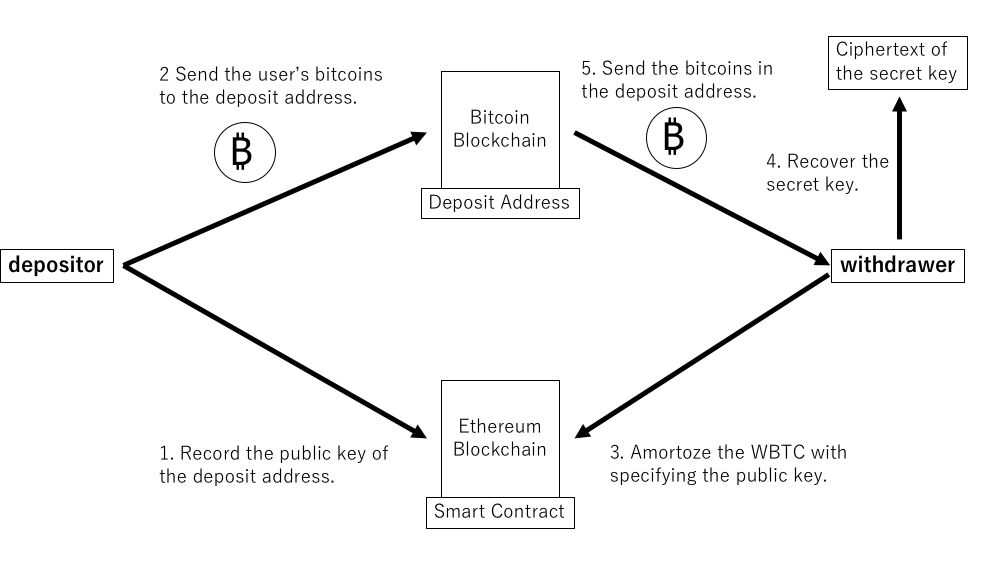
On-Chain vs. Off-Chain Governance: Finding the Right Mix
Blockchain projects often face the choice between on-chain and off-chain governance models. On-chain governance involves making decisions directly on the blockchain, often through voting mechanisms. Off-chain governance, on the other hand, relies on external channels for decision-making. Striking the right mix is vital, balancing the efficiency of off-chain discussions with the security and transparency of on-chain decision-making.
Evolution of Governance Models: Learning from Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
The evolution of governance models can be observed through the rise of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). DAOs operate based on smart contracts, enabling decentralized decision-making. However, they also highlight the challenges, such as the infamous “DAO hack,” emphasizing the importance of continuous improvement and learning in governance frameworks.
Transparency and Accountability: Pillars of Effective Governance
Transparency and accountability form the pillars of effective blockchain governance. Transparent decision-making processes and clear communication ensure that stakeholders are well-informed. Accountability mechanisms, such as smart contracts that automatically execute decisions based on predefined rules, enhance trust and reduce the risk of governance failures.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating Legal Frameworks
As the blockchain space matures, regulatory compliance becomes a critical aspect of governance frameworks. Projects need to navigate legal frameworks and ensure that governance structures align with existing regulations. Striking a balance between decentralization and regulatory compliance is an ongoing challenge that requires collaboration with legal experts.
Adaptability and Upgrades: Flexibility in Governance
Blockchain governance frameworks must be adaptable to changing circumstances and technological advancements. The ability to implement upgrades and improvements is essential for the long-term success of blockchain projects. Governance frameworks should include clear processes for proposing, discussing, and implementing changes.
Community Engagement and Education: Building a Knowledgeable Community
Effective governance goes hand-in-hand with community engagement and education. Governance decisions impact the entire community, and an informed and engaged community is more likely to contribute positively to the decision-making process. Educational initiatives and transparent communication build trust and foster a sense of shared responsibility.
The Path Forward: Continuous Improvement and Collaboration
In conclusion, navigating blockchain governance requires continuous improvement and collaboration. Blockchain projects should view governance frameworks as evolving structures that adapt to the dynamic nature of the industry. By prioritizing decentralization, inclusivity, transparency, and adaptability, blockchain governance frameworks can pave the way for sustainable success.