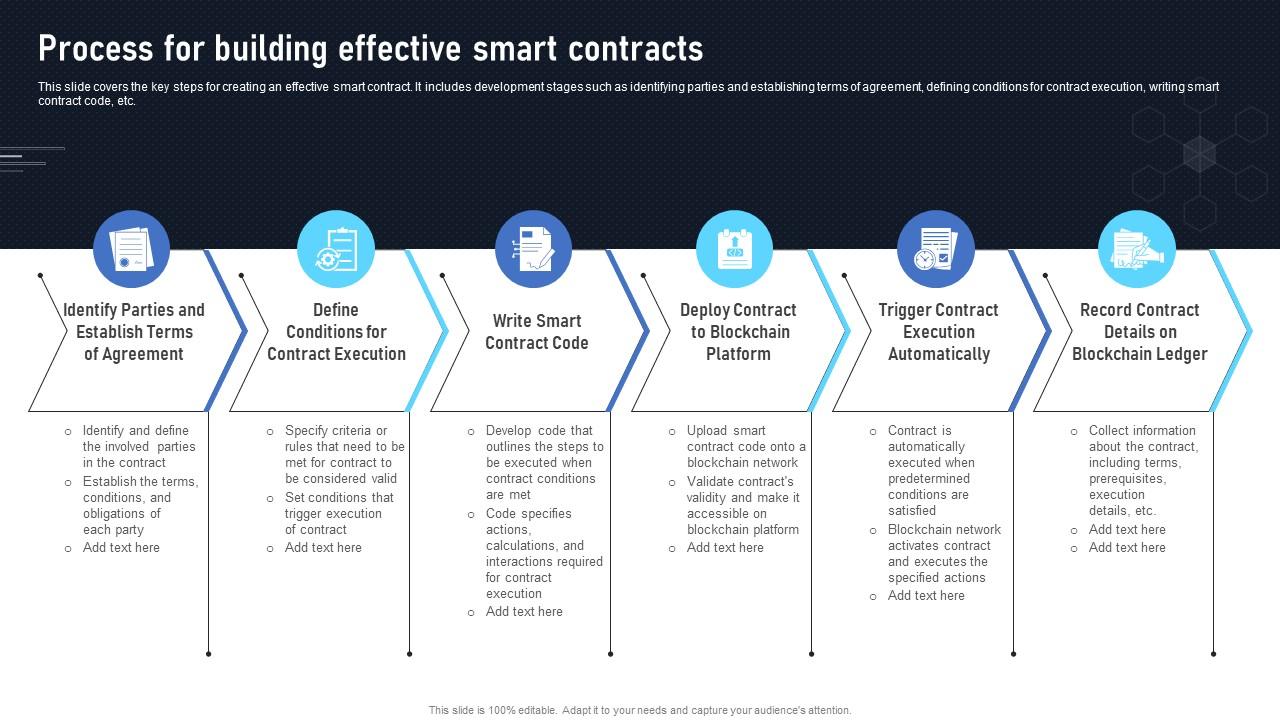
Decentralized Harmony: Exploring Blockchain Consensus Algorithms
Decentralized Harmony: Exploring Blockchain Consensus Algorithms
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we perceive and conduct transactions, offering a decentralized and secure framework. At the heart of this innovation lie consensus algorithms, crucial for maintaining the integrity of the distributed ledger. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of blockchain consensus algorithms, understanding their significance and exploring their diverse implementations.
The Foundation of Blockchain
Blockchain serves as a transparent and tamper-resistant ledger by employing a decentralized network of nodes. Consensus algorithms are the linchpin of this technology, ensuring that all nodes agree on the state of the ledger. Without a centralized authority, these algorithms play a pivotal role in maintaining trust and reliability.
Proof of Work: Pioneering Consensus
The most renowned consensus algorithm, Proof of Work (PoW), was introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in the Bitcoin whitepaper. PoW relies on miners solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. While effective, PoW has faced criticism for its energy-intensive nature, prompting exploration into more sustainable alternatives.
Proof of Stake: Shifting the Paradigm
In response to environmental concerns, Proof of Stake (PoS) emerged as an alternative consensus algorithm. Unlike PoW, PoS doesn’t rely on miners but rather on validators who lock up a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral. Validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold, promoting a more energy-efficient approach.
Delegated Proof of Stake: Streamlining Consensus
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) takes PoS a step further by introducing a governance layer. In DPoS, coin holders vote for a select number of delegates who are responsible for validating transactions and creating blocks. This streamlined approach enhances scalability and efficiency, making DPoS a popular choice for various blockchain projects.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance: Ensuring Security
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) focuses on ensuring consensus in the presence of malicious nodes. It is particularly suitable for permissioned blockchains, where participants are known and trusted. PBFT allows nodes to reach a consensus even if a portion of them behaves maliciously, making it a robust choice for enterprise use cases.
Hybrid Approaches: Balancing Trade-Offs
Hybrid consensus algorithms combine elements from different models to address specific challenges. These approaches aim to strike a balance between decentralization, security, and scalability. By leveraging the strengths of multiple consensus mechanisms, hybrid models offer a nuanced solution tailored to the specific requirements of a blockchain network.
The Evolution Continues
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, researchers and developers explore novel consensus algorithms to address the limitations of existing models. Whether it’s enhancing scalability, mitigating environmental impact, or ensuring security, the quest for optimal consensus mechanisms drives innovation in the blockchain space.
In conclusion, blockchain consensus algorithms form the backbone of decentralized networks, shaping the future of trustless transactions. From the pioneering days of Proof of Work to the energy-efficient landscape of Proof of Stake, and the versatile nature of hybrid approaches, these algorithms play a critical role in defining the functionality and success of blockchain systems.
To delve even deeper into the world of Blockchain Consensus Algorithms, visit Blockchain Consensus Algorithms. Explore the evolving landscape of these algorithms and stay abreast of the latest developments in the dynamic realm of blockchain technology.