Scaling Horizons: Exploring Blockchain’s Growth Techniques
Scaling Horizons: Unveiling Blockchain’s Growth Techniques
Blockchain technology, while revolutionary, faces the challenge of scalability as it grows. This article delves into various blockchain scaling techniques, examining their significance, implementation methods, and the impact they have on fostering a more scalable and efficient decentralized ecosystem.
The Challenge of Scalability in Blockchain
As blockchain networks gain popularity, scalability becomes a critical factor. The original blockchain, Bitcoin, had limitations in terms of transaction speed and throughput. Scalability concerns arise due to the decentralized nature of blockchain, where each participant maintains a copy of the entire ledger, making it challenging to process a large number of transactions quickly.
Off-Chain Scaling Solutions: Lightning Network
One prominent off-chain scaling solution is the Lightning Network. Operating on top of the blockchain, Lightning Network enables faster and more cost-effective transactions by creating off-chain payment channels. Transactions occur off-chain, only settling on the main blockchain when necessary. This technique enhances scalability by reducing the burden on the main blockchain for every transaction.
On-Chain Scaling Approaches: Segregated Witness (SegWit)
Segregated Witness (SegWit) is an on-chain scaling technique adopted by certain blockchains, including Bitcoin. SegWit separates transaction signatures from the transaction data, freeing up space within blocks. This optimization increases the number of transactions that can be included in a block, ultimately improving the scalability of the blockchain.
Sharding: Distributing the Load
Sharding is a technique that involves breaking the blockchain network into smaller, more manageable parts called shards. Each shard operates independently, processing its transactions and smart contracts. This parallel processing significantly improves scalability by allowing multiple transactions to occur simultaneously across different shards. Ethereum 2.0 is exploring sharding as part of its scalability solution.
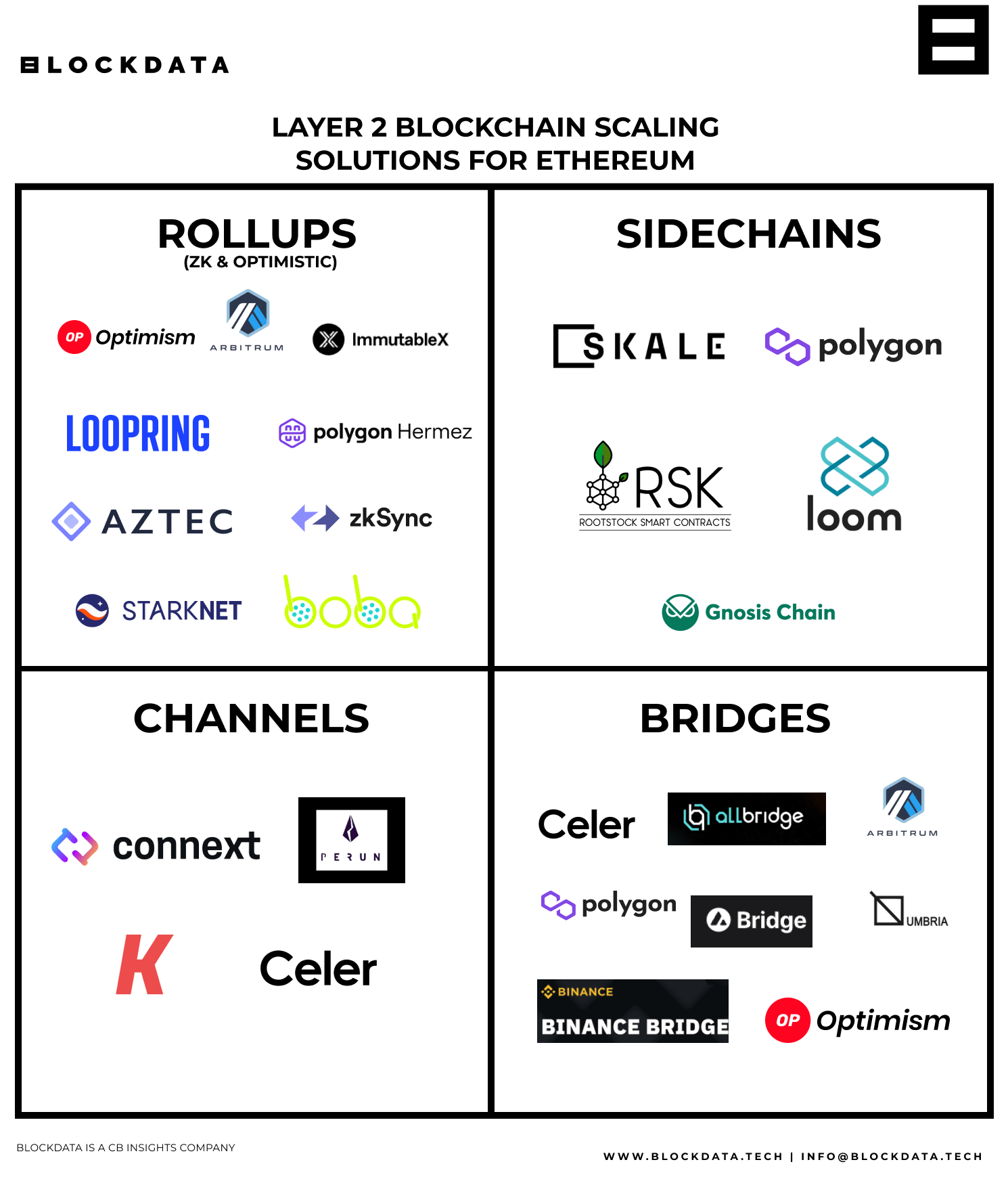
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: State Channels
Layer 2 scaling solutions focus on enhancing scalability without directly impacting the main blockchain. State channels, a type of Layer 2 solution, allow users to conduct off-chain transactions directly with each other. Only the final state is recorded on the main blockchain, reducing congestion and increasing transaction speed. State channels are particularly valuable for applications that require frequent interactions.
Sidechains: Parallel Chains for Specific Needs
Sidechains operate alongside the main blockchain, providing a parallel chain for specific use cases. They enable customized solutions for certain applications without affecting the main network. Sidechains improve scalability by offloading specific transactions, preserving the efficiency of the primary blockchain.
Consensus Algorithm Enhancements: Proof of Stake (PoS)
Consensus algorithms play a pivotal role in scalability. Proof of Stake (PoS) is an alternative to Proof of Work (PoW) that reduces the energy consumption associated with mining. PoS enhances scalability by allowing validators to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
Interoperability: Seamless Collaboration Between Blockchains
Interoperability addresses scalability by fostering collaboration between different blockchains. By allowing communication and transfer of value between diverse networks, interoperability enhances scalability and opens the door to a more connected blockchain ecosystem.
Optimistic Rollups: Balancing Security and Scalability
Optimistic Rollups are Layer 2 scaling solutions that strike a balance between security and scalability. They process transactions off-chain but periodically submit a summary of those transactions to the main blockchain. This approach optimizes efficiency while maintaining the security benefits of the underlying blockchain.
Blockchain Scaling Techniques at fireboyandwatergirlplay.com
For in-depth insights into blockchain scaling techniques and updates on the latest developments, visit Blockchain Scaling Techniques. This platform serves as a valuable resource, offering a comprehensive overview of diverse scaling methods shaping the future of blockchain scalability.
Conclusion: Scaling for a Decentralized Future
In conclusion, blockchain scaling techniques are crucial for ensuring the continued growth and efficiency of decentralized networks. As blockchain technology evolves, the implementation of innovative scaling solutions becomes imperative. By exploring and adopting these techniques, the blockchain community paves the way for a decentralized future that is not only secure and scalable but also capable of supporting a wide array of applications and use cases.