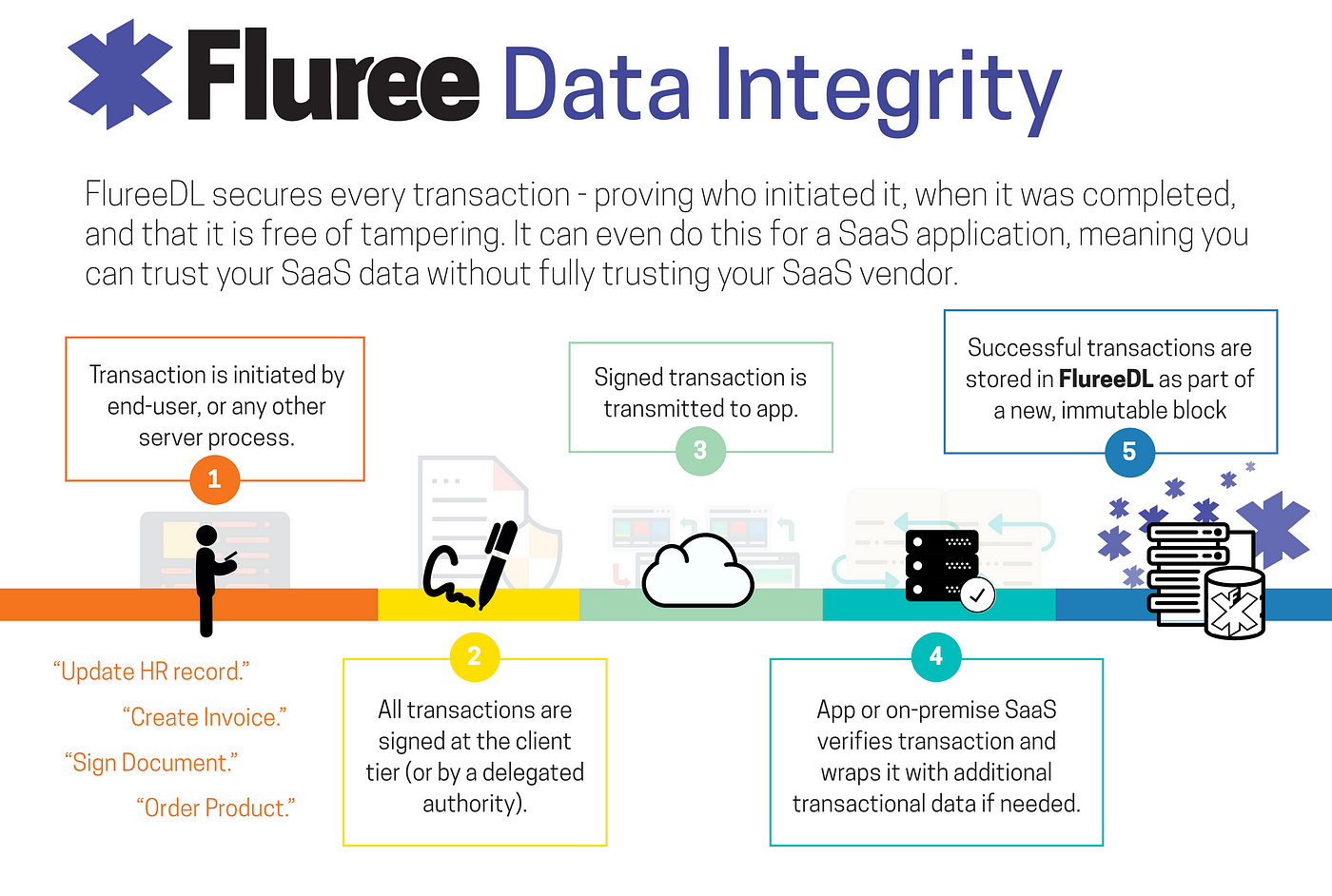
A Blockchain is a Type of Distributed Ledger Technology
Understanding How a Blockchain is a Type of Distributed Ledger Technology
Demystifying Blockchain Technology
In the digital age, blockchain technology has emerged as a buzzword, promising revolutionary changes across various industries. At its core, a blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology, offering a decentralized and transparent approach to recording transactions. However, the intricacies of blockchain can often seem complex and daunting. Let’s delve deeper into the fundamentals of blockchain technology to gain a clearer understanding of its inner workings.
Decentralization: The Foundation of Blockchain
One of the key principles of blockchain technology is decentralization. Unlike traditional centralized systems where data is stored and controlled by a single entity, blockchain operates on a network of computers, known as nodes. Each node in the network maintains a copy of the blockchain, ensuring that no single point of failure exists. This decentralized architecture enhances security, resilience, and trust in the system, as there is no central authority governing the network.
Immutable Record-Keeping: Ensuring Data Integrity
Another fundamental feature of blockchain technology is its immutable nature. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This is achieved through cryptographic techniques, where each block in the blockchain contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a chain of blocks that is resistant to tampering. This ensures the integrity and immutability of the data stored on the blockchain, making it an ideal solution for applications requiring secure and transparent record-keeping.
Transparency and Trust: Building Confidence in Transactions
Transparency is another hallmark of blockchain technology. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants in the network, ensuring transparency and accountability. This transparency fosters trust among participants, as they can verify the authenticity and validity of transactions in real-time. Additionally, blockchain technology eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation in transactions.
Cryptocurrency Infrastructure: The Rise of Digital Assets
One of the most well-known applications of blockchain technology is cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum utilize blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. Blockchain serves as the underlying infrastructure for cryptocurrencies, providing a secure and decentralized platform for conducting digital transactions. The advent of cryptocurrencies has revolutionized the financial landscape, offering an alternative to traditional fiat currencies and banking systems.
Innovative Solutions: Beyond Cryptocurrencies
While cryptocurrencies have garnered much attention, the potential applications of blockchain technology extend far beyond digital currencies. Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems. By leveraging blockchain technology, organizations can streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance transparency and accountability. Smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and tokenization of assets are just a few examples of innovative solutions enabled by blockchain technology.
Exploring Use Cases: Real-World Applications of Blockchain
In recent years, we have witnessed a proliferation of real-world applications of blockchain technology. In supply chain management, blockchain enables end-to-end visibility and traceability of products, reducing counterfeiting and ensuring authenticity. In healthcare, blockchain facilitates secure and interoperable sharing of patient records, improving data privacy and healthcare outcomes. From digital identity management to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, the potential use cases of blockchain technology are vast and diverse.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Future of Blockchain
While blockchain technology holds immense promise, it also presents challenges and opportunities. Scalability, interoperability, and regulatory compliance are some of the key challenges facing blockchain adoption. However, with ongoing research and development, these challenges can be addressed, unlocking new opportunities for innovation and growth. As we navigate the future of blockchain technology, collaboration, education, and regulatory clarity will be crucial in realizing its full potential across various industries and sectors. Read more about a blockchain is a type of