Blockchain Token Standards: Interoperability and Compatibility

Introduction
Blockchain token standards play a pivotal role in the interoperability and compatibility of tokens across various blockchain platforms. This article explores the significance of Blockchain Token Standards, shedding light on how these standards contribute to the seamless integration and functionality of tokens within the broader blockchain ecosystem.
To explore more about Blockchain Token Standards, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com. This resource offers additional insights, discussions, and community resources on the latest trends in blockchain tokenization.
Understanding Tokenization on the Blockchain
Tokenization involves representing real-world assets or rights on the blockchain through the creation of digital tokens. These tokens can represent anything from currencies and commodities to real estate and digital assets. Blockchain token standards provide a common framework and set of rules that enable these tokens to be created, managed, and transferred across different blockchain networks.
ERC-20: The Universal Token Standard
One of the most well-known and widely adopted blockchain token standards is ERC-20 (Ethereum Request for Comment 20). ERC-20 defines a set of rules and functions that a token contract on the Ethereum blockchain must implement to be considered ERC-20 compliant. This standard has become a cornerstone for the majority of initial coin offerings (ICOs) and token issuances on the Ethereum platform.
ERC-721: NFTs and Unique Token Standards
While ERC-20 is suitable for fungible tokens (those that are interchangeable with each other), ERC-721 introduces a standard for non-fungible tokens (NFTs). NFTs represent unique assets, and each token has distinct properties. This standard gained prominence in the world of digital art, collectibles, and gaming, where the uniqueness and ownership of specific assets are crucial.
Cross-Chain Compatibility and Blockchain Bridges
As the blockchain ecosystem expands, the need for cross-chain compatibility becomes evident. Blockchain token standards that support interoperability facilitate the movement of tokens across different blockchain networks. Projects and initiatives focusing on blockchain bridges aim to create seamless connections between various blockchains, enabling assets to flow securely between them.
Emerging Standards and Innovations
The blockchain space is dynamic, and new token standards continue to emerge. Innovations such as ERC-1155 introduce a multi-token standard, allowing a single contract to manage multiple types of tokens. This not only streamlines the development process but also offers more flexibility in creating diverse tokenized ecosystems.
To explore more about the latest Blockchain Token Standards, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com. Stay updated on emerging standards and innovations shaping the future of blockchain tokenization.
Challenges in Token Standardization
Despite the advantages of having standards, challenges exist in the realm of token standardization. Different blockchain platforms may have their unique standards, leading to fragmentation. Efforts to create universally accepted standards that work seamlessly across various blockchains are ongoing, with the aim of fostering a more interconnected and accessible tokenized ecosystem.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
As the adoption of blockchain tokens increases, regulatory scrutiny also intensifies. Blockchain token standards need to consider regulatory requirements to ensure compliance. Projects must navigate the complex regulatory landscape to avoid legal complications and maintain the legitimacy of their tokenized offerings.
Community Collaboration and Governance
The development and evolution of blockchain token standards often involve community collaboration. Governance mechanisms within blockchain projects allow token holders to participate in decision-making processes, including proposing and voting on changes to standards. This democratic approach contributes to the adaptability and resilience of token standards.
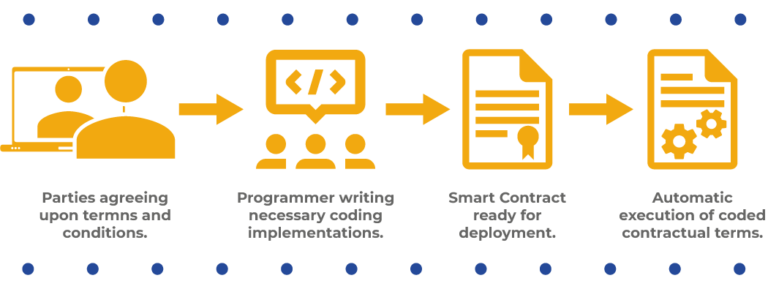
Integration with Smart Contracts and DApps
Smart contracts are integral to the functionality of blockchain tokens. Token standards define the structure and behavior of these smart contracts, ensuring consistency and compatibility. Decentralized applications (DApps) built on blockchain platforms can seamlessly interact with tokens following established standards, creating a vibrant and interconnected ecosystem.
Future Outlook and Standard Evolution
The future of blockchain token standards holds promises of further evolution and standardization. Ongoing efforts to improve interoperability, address scalability issues, and enhance security will shape the next generation of token standards. As blockchain technology continues to mature, standardized tokenization will likely play a pivotal role in the broader adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) and tokenized assets.
Conclusion
Blockchain Token Standards form the backbone of tokenization, enabling the creation and management of digital assets on the blockchain. From fungible tokens like ERC-20 to unique NFTs governed by ERC-721, these standards provide the necessary framework for interoperability and seamless integration. As the blockchain space evolves, ongoing collaboration, regulatory considerations, and technological advancements will define the future landscape of token standards, fostering a more accessible and interconnected decentralized ecosystem.