Explore VR on iPhone 12 Immersive Experiences Await

Unlocking the Potential of VR on iPhone 12: A Gateway to Immersive Experiences
Exploring the Evolution of VR on iPhone 12
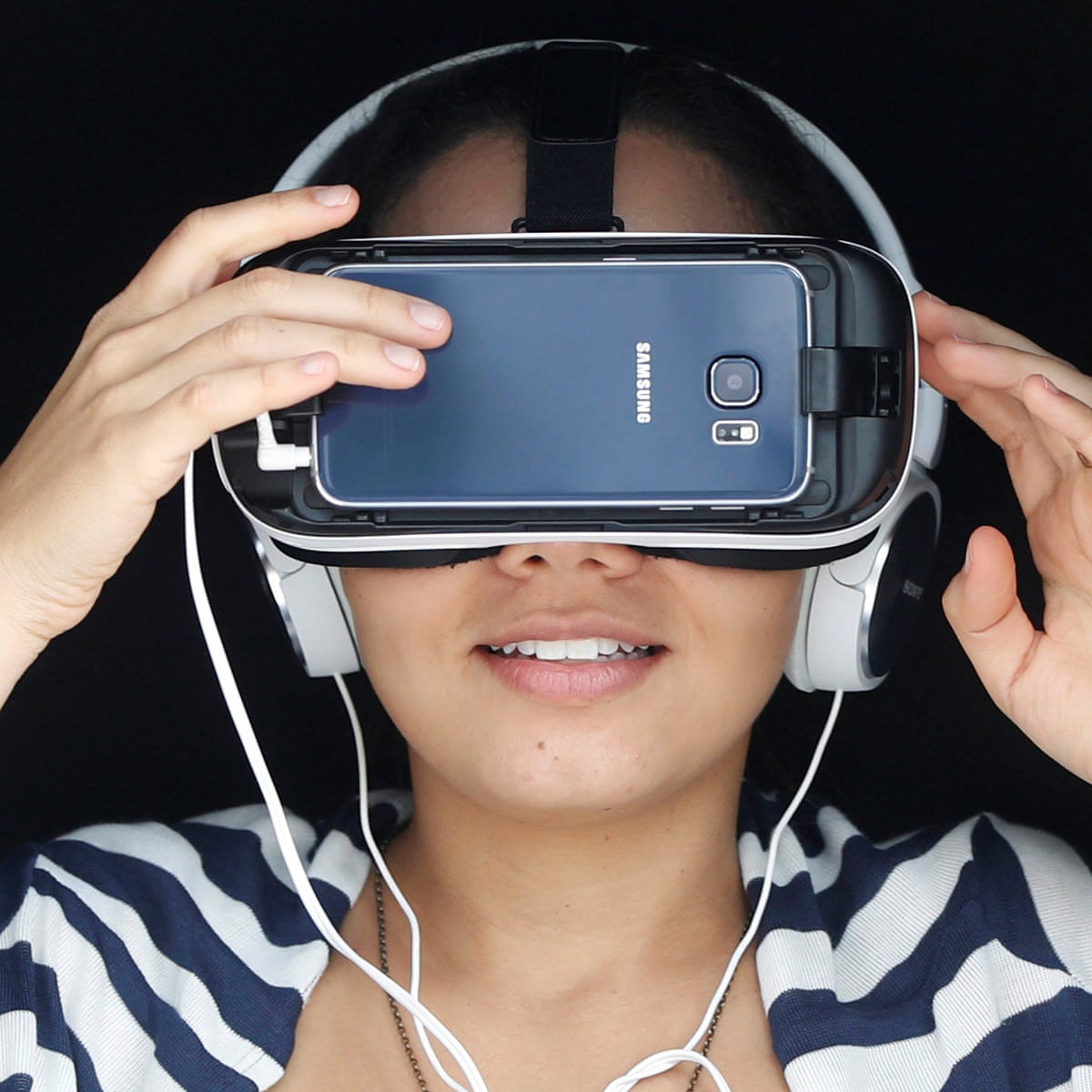
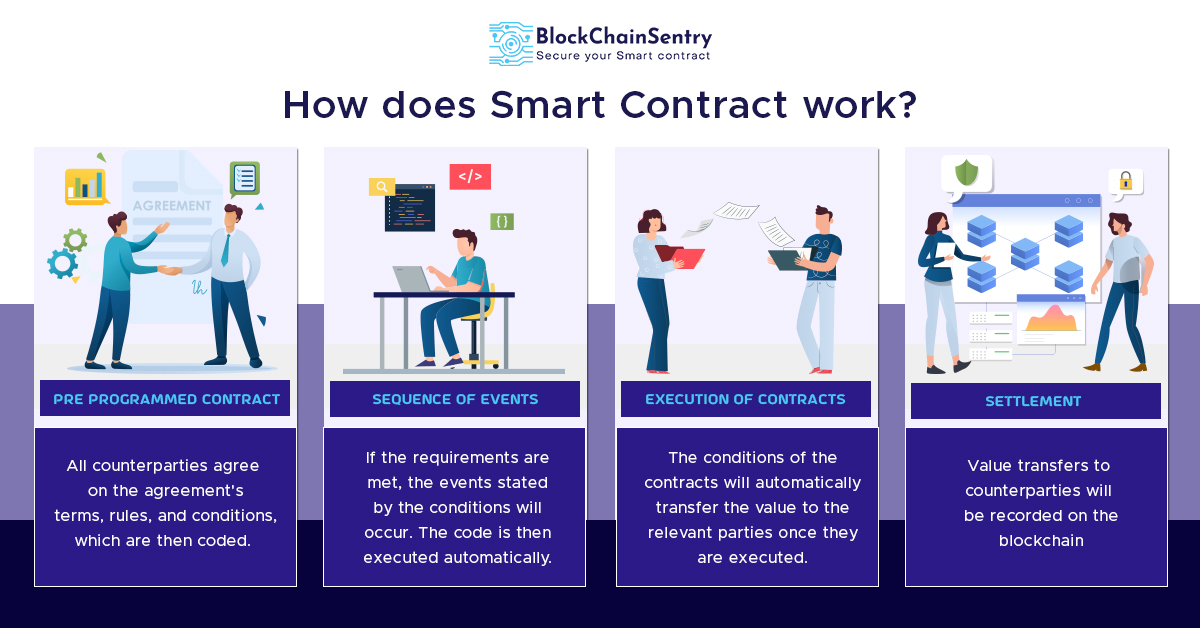
In the realm of technology, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a transformative force, and the iPhone 12 stands at the forefront of this evolution. With its powerful hardware and cutting-edge capabilities, the iPhone 12 offers users a gateway to immersive VR experiences like never before. Let’s delve into the world of VR on iPhone 12 and explore its potential.
Immersive Adventures Await
One of the most captivating aspects of VR on iPhone 12 is the immersive experiences it offers. From exploring virtual landscapes to engaging in interactive games, users can dive into a world of endless possibilities. The high-resolution display and powerful graphics capabilities of the iPhone 12 ensure that every moment in VR feels lifelike and engaging.
Unleashing Creativity and Imagination
With VR on iPhone 12, users are not just consumers of content; they are creators. The iPhone 12 provides tools and platforms for users to unleash their creativity and imagination in VR. Whether designing virtual spaces, creating immersive storytelling experiences, or developing interactive applications, the possibilities are limitless.
Transforming Entertainment and Education
VR on iPhone 12 is revolutionizing entertainment and education. From immersive gaming experiences to virtual tours of historical landmarks, the iPhone 12 offers a new way to engage with content. Educators are leveraging VR on iPhone 12 to create immersive learning experiences that bring subjects to life and captivate students’ attention in ways traditional methods cannot.
Exploring New Realms
One of the most exciting aspects of VR on iPhone 12 is the ability to explore new realms and dimensions. Whether it’s diving into the depths of the ocean, soaring through space, or traversing fantastical landscapes, the iPhone 12 allows users to escape reality and enter a world of endless adventure. With VR on iPhone 12, the only limit is your imagination.
Enhancing Productivity and Collaboration
Beyond entertainment, VR on iPhone 12 is also enhancing productivity and collaboration. Virtual meetings and collaborative workspaces enable teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of their physical location. Whether it’s brainstorming ideas, reviewing designs, or conducting training sessions, VR on iPhone 12 offers new ways to collaborate and communicate.
Pushing the Boundaries of Innovation
The iPhone 12 is not just a device; it’s a platform for innovation. Developers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with VR on iPhone 12, creating groundbreaking applications and experiences that redefine how we interact with technology. From healthcare and engineering to entertainment and beyond, VR on iPhone 12 is driving innovation across industries.
Embracing the Future of Technology
As we look to the future, VR on iPhone 12 represents a glimpse of what’s to come. With advancements in hardware and software, the possibilities for VR on iPhone 12 are endless. Whether it’s exploring virtual worlds, creating immersive experiences, or collaborating with colleagues, the iPhone 12 is shaping the future of technology and redefining the way we interact with the digital world. Read more about vr iphone 12