Seamless Blockchain Integration: Strategic Approaches
Navigating the Path to Seamless Blockchain Integration
The adoption of blockchain technology across industries is gaining momentum, but successful integration requires careful planning and strategic approaches. In this article, we explore key strategies for achieving seamless blockchain integration and unlocking the full potential of decentralized solutions.
Understanding the Landscape: Blockchain Basics
Before delving into integration strategies, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of blockchain basics. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data. Its decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, making it an attractive solution for various applications.
Identifying Integration Objectives: Define Your Goals
Every organization considering blockchain integration must clearly define its objectives. Whether aiming to streamline operations, enhance transparency, or improve security, setting clear goals provides a roadmap for selecting the most appropriate blockchain solutions. Understanding the unique needs of your business is fundamental to successful integration.
Choosing the Right Blockchain Platform: Tailoring Solutions to Your Needs
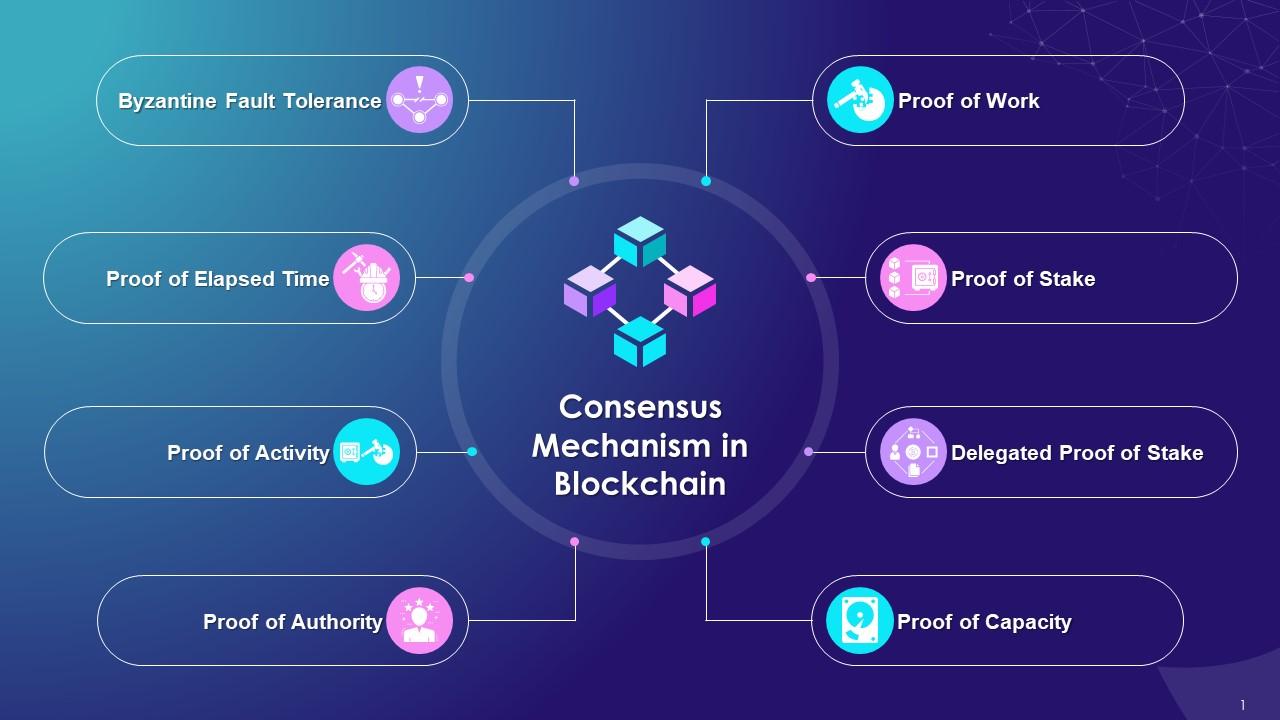
Selecting the right blockchain platform is a critical decision in the integration process. Consider factors such as scalability, consensus mechanisms, and smart contract capabilities. Whether it’s Ethereum, Hyperledger, or a bespoke solution, choosing a platform that aligns with your specific requirements is key to a successful integration.
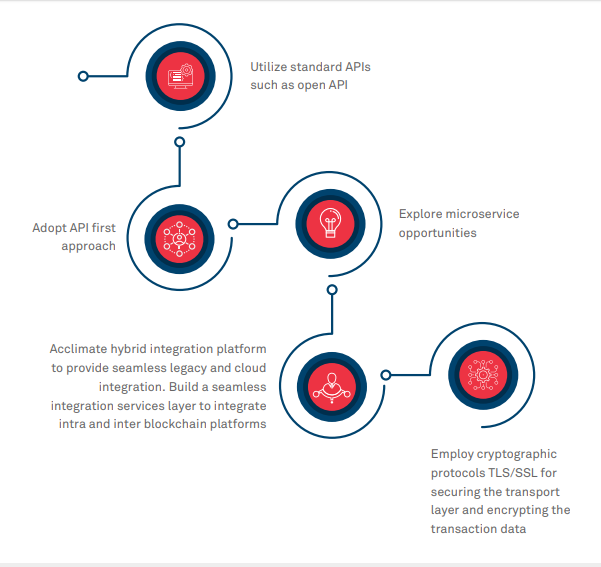
Interoperability: Bridging the Gap Between Systems
Achieving interoperability is essential for seamless integration, especially in complex business environments. Blockchain integration should not create silos; instead, it should seamlessly connect with existing systems. Standardization efforts and the use of interoperability protocols contribute to a cohesive and interconnected technological landscape.
Smart Contract Implementation: Automating Processes
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. Leveraging smart contracts automates processes, reduces the risk of errors, and enhances efficiency. Integrating smart contracts into existing workflows can streamline operations and unlock new possibilities for automation.
Security Measures: Prioritizing Data Protection
Blockchain’s reputation for security is a key driver of its adoption. However, integrating blockchain doesn’t absolve the need for robust security measures. Implementing encryption, access controls, and regular audits are crucial to safeguarding sensitive data. A comprehensive security strategy ensures the trustworthiness of the integrated blockchain solution.
User Training and Adoption: Empowering Your Team
Successful blockchain integration extends beyond technology; it involves people. Providing adequate training to your team is vital for smooth adoption. Employees should understand the benefits of blockchain, its impact on their roles, and how to navigate the integrated systems. Empowering your team with the necessary skills fosters a positive transition.
Scalability Planning: Preparing for Growth
Scalability is a consideration that should not be overlooked. As your organization grows, so will the demands on the blockchain network. Planning for scalability involves choosing solutions that can handle increased transactions and data volumes. Future-proofing your integration ensures sustained success in the long run.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Iterative Improvement
The integration process doesn’t end with the initial setup. Continuous monitoring and optimization are crucial for identifying potential issues and fine-tuning the integrated system. Regular assessments enable organizations to adapt to evolving technological landscapes and stay ahead in the rapidly changing blockchain ecosystem.
Blockchain Integration in Action: Realizing the Benefits
As organizations navigate the complexities of blockchain integration, successful implementation yields tangible benefits. Enhanced efficiency, increased transparency, and improved security are just a few of the advantages. By strategically integrating blockchain solutions, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of technological innovation.