Elevating Systems: Blockchain Protocol Development Mastery
Pioneering Excellence: Navigating Blockchain Protocol Development
Blockchain protocol development stands as the bedrock of decentralized systems, laying the foundation for secure, transparent, and trustless digital interactions. This article takes a comprehensive journey into the intricacies of blockchain protocol development, exploring its significance, the development process, and its transformative impact on the digital landscape.
The Significance of Blockchain Protocols
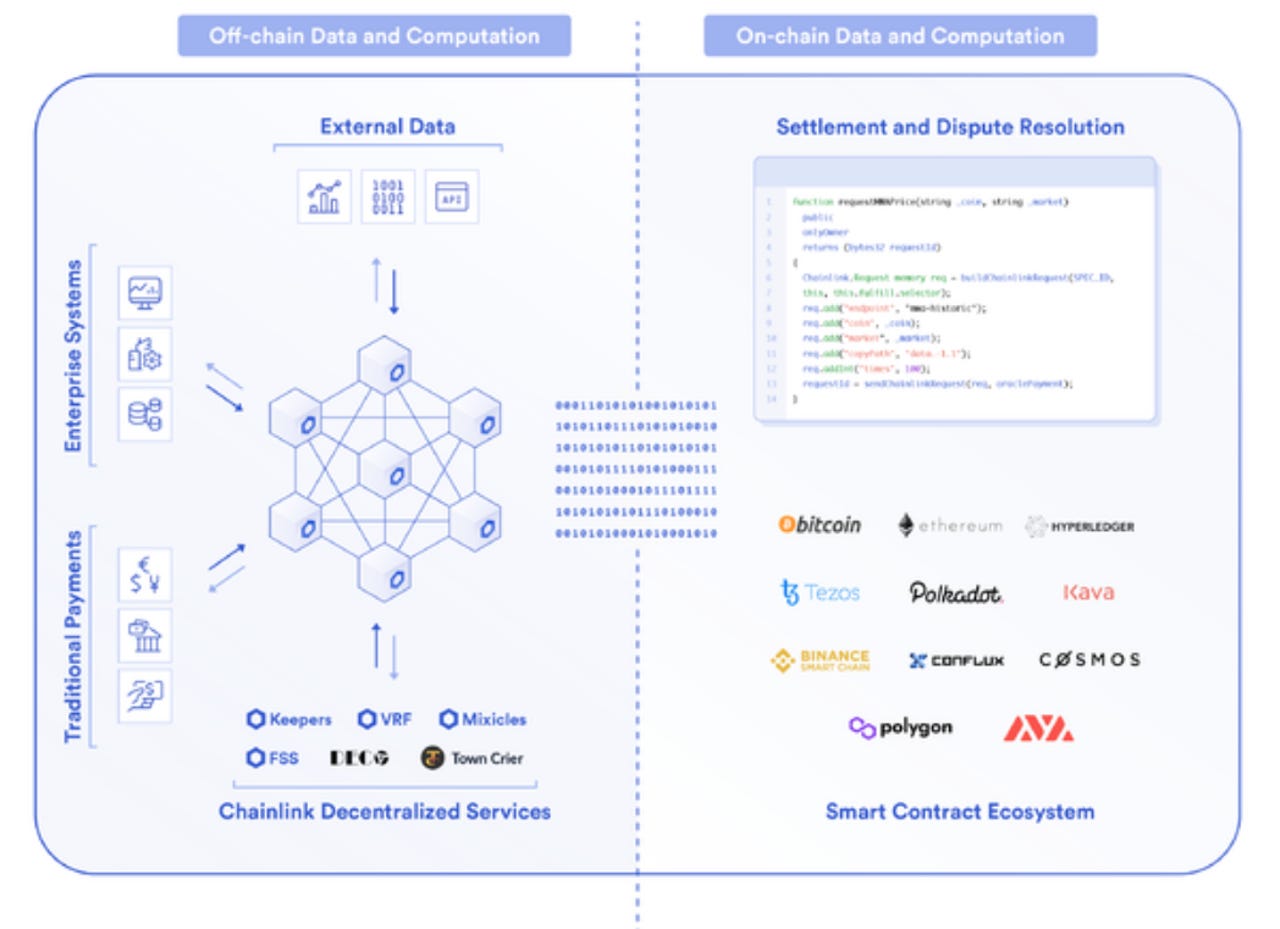
Blockchain protocols serve as the governing rules that define how a blockchain network operates. They determine consensus mechanisms, data validation processes, and the overall structure of the decentralized ecosystem. The significance of a robust and well-designed protocol cannot be overstated, as it directly influences the security, scalability, and efficiency of the blockchain network.
Decentralization and Trustlessness at the Core
At the heart of blockchain protocol development lies the pursuit of decentralization and trustlessness. These protocols aim to eliminate the need for central authorities, fostering a distributed network where participants collectively validate transactions. The trustless nature ensures that parties can interact securely without reliance on intermediaries, reshaping traditional paradigms of digital trust.
Consensus Mechanisms: The Pillars of Trust
Consensus mechanisms, a crucial component of blockchain protocols, determine how nodes agree on the state of the network. From Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) and newer models like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), each mechanism has its strengths and considerations. The choice of consensus mechanism profoundly impacts the security, scalability, and energy efficiency of the blockchain.
Smart Contracts: The Logic of Execution
Blockchain protocols often support smart contracts, self-executing contracts with coded logic. Smart contracts enable the automation of predefined actions when specific conditions are met, fostering programmable and decentralized applications. The development of robust smart contract functionality within a protocol opens avenues for a diverse range of decentralized applications (DApps).
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Protocols
As the blockchain ecosystem expands, the need for interoperability between different blockchain networks becomes paramount. Cross-chain protocols facilitate communication and value transfer between disparate blockchains. These developments not only enhance connectivity but also contribute to the creation of a more cohesive and collaborative decentralized landscape.
Security Challenges and Audits in Protocol Development
Blockchain protocol development is not without challenges, particularly in terms of security. The immutable and transparent nature of the blockchain means that vulnerabilities can have far-reaching consequences. Rigorous security audits, continuous testing, and adherence to best practices are integral to mitigating risks and ensuring the resilience of the developed protocols.
Tokenization Protocols and Asset Representation
Many blockchain protocols support tokenization, the process of representing real-world assets as digital tokens on the blockchain. Tokenization protocols enable the creation and management of these digital assets, paving the way for efficient and transparent ownership of a wide array of assets, from real estate to artwork.
The Evolution of Blockchain Protocols
Blockchain protocol development is a dynamic field witnessing continuous evolution. From the early days of Bitcoin to the emergence of Ethereum and the subsequent development of various blockchain platforms, the landscape is constantly evolving. Newer protocols aim to address scalability issues, enhance privacy features, and incorporate innovative consensus mechanisms, driving the industry forward.
Community Collaboration and Open Source Development
The development of blockchain protocols often thrives on community collaboration and open-source contributions. Many protocols are developed collaboratively, with a community of developers contributing code, providing feedback, and collectively steering the direction of the protocol’s evolution. This open and collaborative approach reflects the decentralized ethos of blockchain technology.
Exploring Blockchain Protocol Development
For an in-depth exploration of blockchain protocol development and its transformative potential, visit Blockchain Protocol Development. Dive into the nuances of consensus mechanisms, smart contract execution, and the security considerations that shape the development landscape. It’s an invitation to engage with the intricacies of blockchain protocol development and witness the ongoing revolution in decentralized systems.