Seamless Tokens: Navigating Cross-Chain Transfers
Seamless Tokens: Navigating Cross-Chain Transfers
Cross-chain token transfers have emerged as a pivotal innovation in the blockchain space, enabling seamless movement of digital assets across different blockchain networks. This article explores the intricacies of cross-chain token transfers, examining their significance, underlying technologies, and potential impact on the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Understanding Cross-Chain Token Transfers
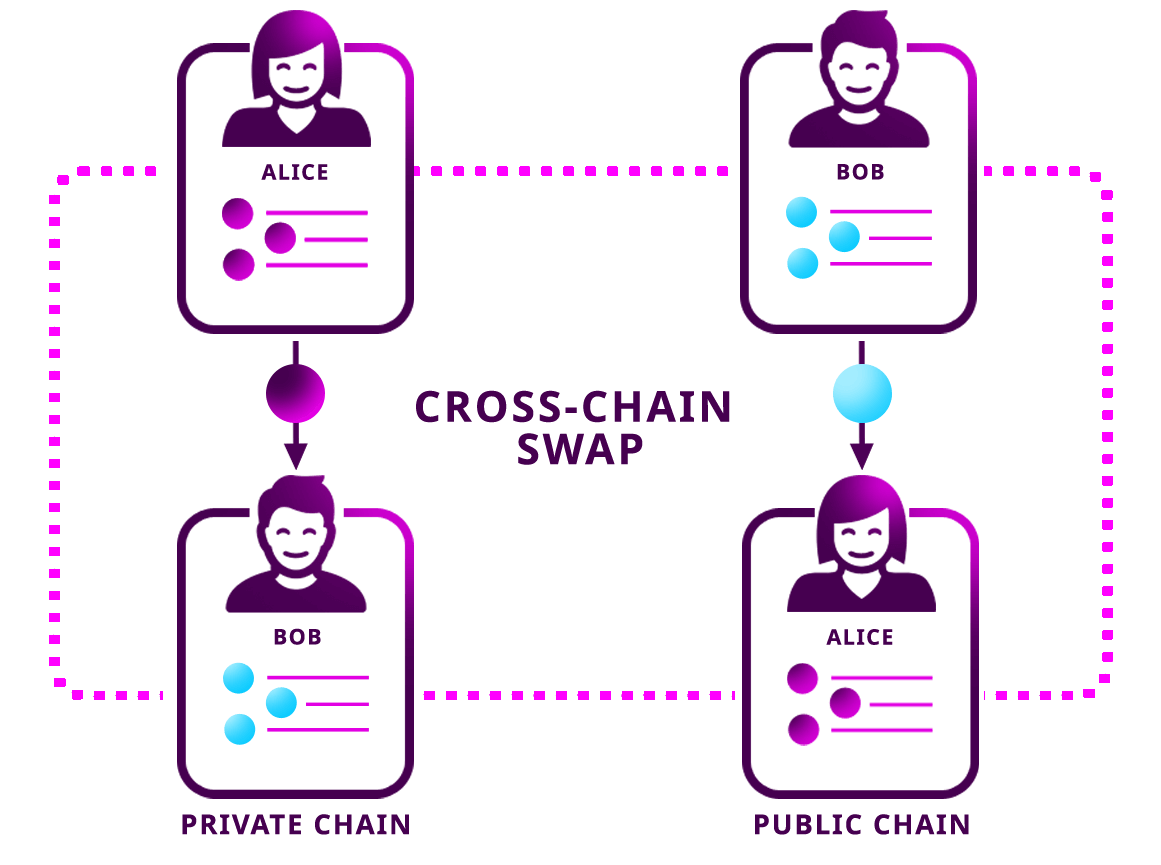
Cross-chain token transfers involve the movement of tokens or assets from one blockchain network to another. Traditional blockchain networks operate in isolation, limiting the interoperability of digital assets. Cross-chain solutions aim to overcome this limitation, facilitating the transfer of tokens across disparate blockchain networks, fostering collaboration, and enhancing the overall functionality of decentralized ecosystems.
Interoperability Challenges in Blockchain
Interoperability has long been a challenge in the blockchain space. Different blockchain networks often use unique protocols, consensus mechanisms, and smart contract standards, creating siloed environments. Cross-chain token transfers address this challenge by establishing protocols and technologies that enable communication and asset exchange between diverse blockchain networks.
Key Technologies Powering Cross-Chain Transfers
Several technologies contribute to the success of cross-chain token transfers. Atomic swaps, a trustless mechanism that allows users to exchange tokens across different blockchains without the need for an intermediary, play a crucial role. Additionally, interoperability protocols like Polkadot and Cosmos provide frameworks for cross-chain communication, enabling seamless transactions.
Enhancing Liquidity and Accessibility
Cross-chain token transfers significantly enhance liquidity in the blockchain ecosystem. By allowing assets to move freely between different chains, users can access a broader range of decentralized applications (DApps) and financial services. This increased accessibility contributes to a more vibrant and interconnected blockchain landscape.
Benefits for Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) stands to gain substantial benefits from cross-chain token transfers. Liquidity pools, lending platforms, and other DeFi applications can tap into a more extensive pool of assets from various blockchain networks. This not only diversifies the range of available assets but also mitigates risks associated with single-chain dependencies.
Security Considerations in Cross-Chain Transfers
While cross-chain transfers offer increased functionality, security considerations are paramount. Ensuring the integrity of the transferred assets and protecting against potential vulnerabilities during the transfer process is crucial. Smart contract audits, robust cryptographic protocols, and thorough testing are essential steps in mitigating security risks.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Cross-chain token transfers find practical applications in various use cases. From enabling cross-border payments to facilitating asset tokenization, the technology opens new avenues for innovation. Gaming platforms, supply chain solutions, and identity management systems can all benefit from the seamless transfer of tokens across different blockchain networks.
Industry Collaboration and Standardization
The successful implementation of cross-chain token transfers requires industry collaboration and standardization. Efforts by organizations like the Interledger Protocol (ILP) and the Blockchain Interoperability Alliance aim to establish common standards and protocols that facilitate cross-chain communication. Standardization is vital for ensuring a cohesive and interoperable blockchain ecosystem.
The Future Landscape of Cross-Chain Token Transfers
As the blockchain space continues to evolve, the future landscape of cross-chain token transfers holds significant promise. Continued research and development, along with industry collaboration, will likely lead to more advanced cross-chain solutions. The integration of cross-chain transfers may become a standard feature, further enhancing the overall efficiency and interoperability of blockchain networks.
Exploring Cross-Chain Token Transfers – Learn More
To delve deeper into Cross-Chain Token Transfers, visit fireboyandwatergirlplay.com. This comprehensive resource offers additional insights, tutorials, and updates on the latest developments in the world of cross-chain transfers and their impact on the blockchain ecosystem.
In conclusion, cross-chain token transfers represent a pivotal step towards creating a more interconnected and versatile blockchain landscape. The ability to seamlessly move assets across different blockchain networks opens new possibilities for decentralized applications, finance, and beyond. As the technology matures, cross-chain transfers are poised to play a central role in shaping the future of blockchain interoperability.

:format(jpg)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/coindesk/F5XNBUIGJFAR5BNZGXAWTZC5OM.jpg)