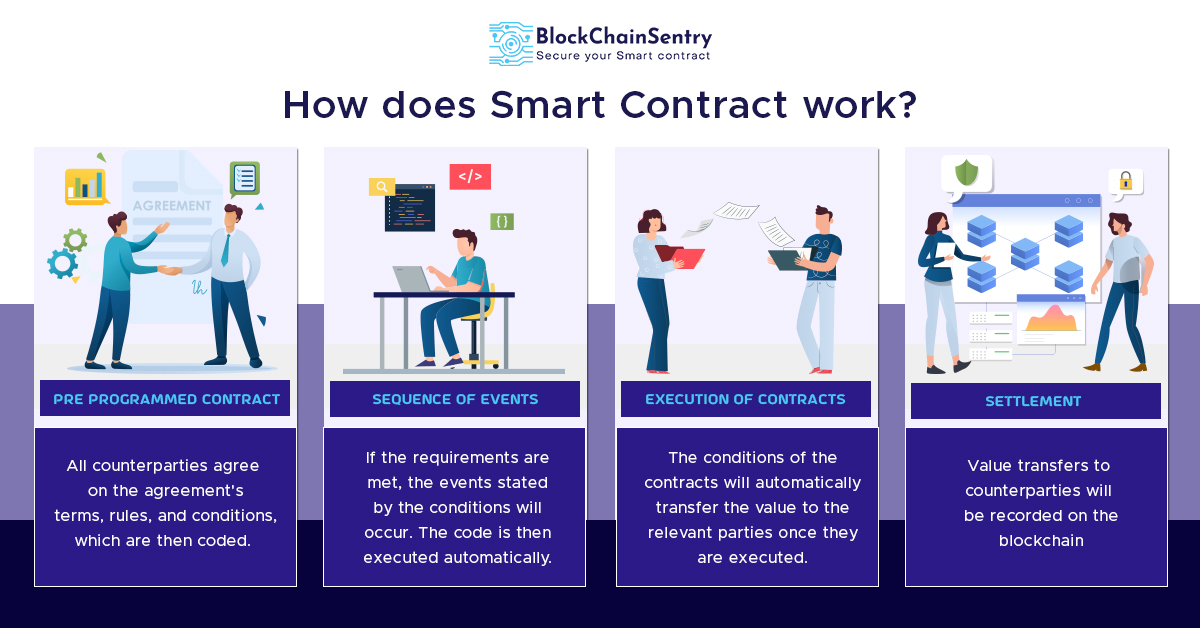
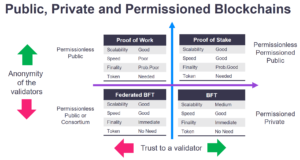
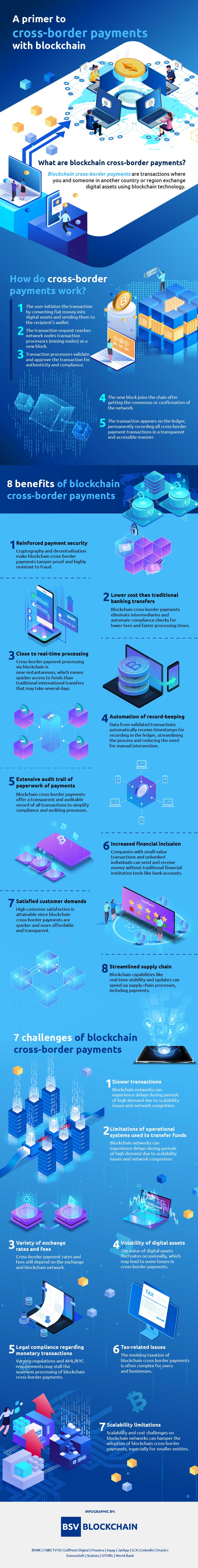
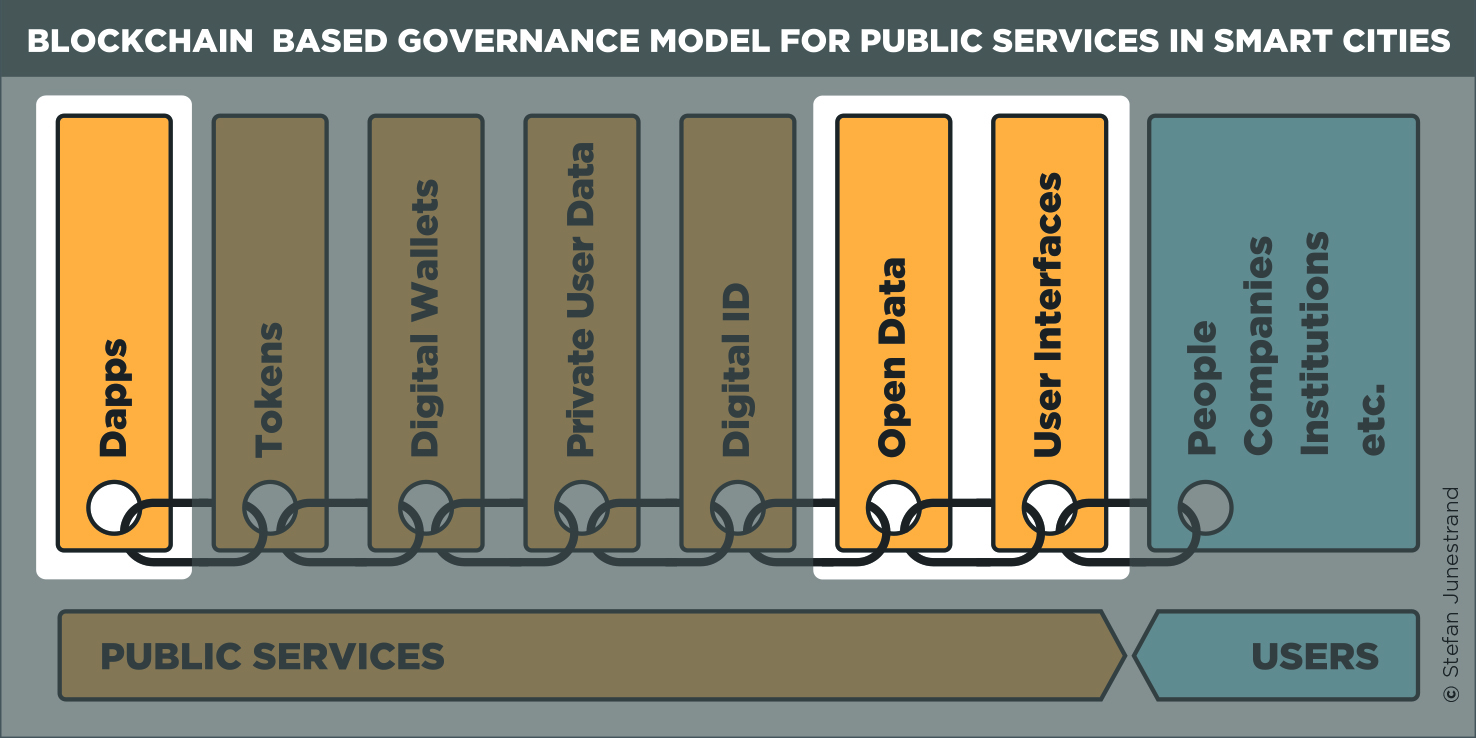
Securing Networks: Byzantine Fault Tolerance Models
Ensuring Reliability: Navigating Byzantine Fault Tolerance Models
In the complex landscape of distributed systems, Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) models stand as a cornerstone, providing robust solutions to mitigate the challenges posed by malicious actors. Let’s delve into the intricacies of Byzantine Fault Tolerance models and their pivotal role in securing networks.
Understanding Byzantine Fault Tolerance: Defending Against Malicious Actors
Byzantine Fault Tolerance is a concept rooted in distributed computing, specifically addressing the challenges presented by Byzantine failures—situations where nodes in a network may exhibit arbitrary and potentially malicious behavior. BFT models are designed to ensure the system’s integrity and functionality even when a portion of nodes behaves maliciously.
The Byzantine Generals Problem: A Fundamental Challenge
At the heart of Byzantine Fault Tolerance is the Byzantine Generals Problem, a thought experiment illustrating the challenges of achieving consensus among distributed entities in the presence of traitorous actors. BFT models seek to solve this problem by creating mechanisms that enable nodes to reach agreement, even when some nodes provide incorrect or conflicting information.
Classic BFT Models: Paxos and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
Two classical BFT models, Paxos and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), have played pivotal roles in the evolution of distributed systems. Paxos, proposed by Leslie Lamport, focuses on achieving consensus in asynchronous systems. PBFT, on the other hand, introduced by Castro and Liskov, optimizes consensus for practical, real-world scenarios, making it a cornerstone in BFT research.
Optimizing for Performance: HoneyBadgerBFT and Tendermint
As the demand for high-performance BFT models grew, newer solutions emerged. HoneyBadgerBFT and Tendermint represent advancements in optimizing Byzantine Fault Tolerance for improved performance. HoneyBadgerBFT introduces cryptographic techniques to achieve asynchronous BFT, while Tendermint focuses on scalability and usability in practical blockchain applications.
Blockchain and BFT: Enhancing Security in Distributed Ledgers
The integration of Byzantine Fault Tolerance models with blockchain technology has become a paradigm shift in the security of distributed ledgers. Blockchain networks often face malicious actors attempting to compromise the integrity of the ledger. BFT models provide the necessary defense mechanisms to ensure consensus and prevent malicious nodes from disrupting the system.
Asynchronous BFT: Overcoming the Challenges of Timing
One of the challenges in BFT is achieving consensus in asynchronous systems, where nodes operate without synchronized clocks. Asynchronous BFT models, such as HoneyBadgerBFT, utilize cryptographic techniques to overcome timing challenges, allowing nodes to reach consensus without relying on strict time synchronization.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining BFT with Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Hybrid approaches, combining Byzantine Fault Tolerance with consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS), aim to harness the strengths of different models. This integration enhances the overall security and performance of distributed systems, providing a balanced approach to consensus in blockchain networks.
Challenges and Considerations: Scalability and Network Dynamics
While Byzantine Fault Tolerance models offer robust security solutions, challenges remain. Scalability is a primary consideration, especially as blockchain networks grow in size. Additionally, the dynamic nature of network conditions poses challenges for BFT models to adapt and maintain consensus in real-time.
Future Directions: Innovations in Byzantine Fault Tolerance Research
The field of Byzantine Fault Tolerance is dynamic, with ongoing research pushing the boundaries of innovation. New models and protocols continue to emerge, addressing the challenges posed by evolving network dynamics, scalability requirements, and the quest for even more efficient consensus mechanisms.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance Models: A Link to Network Resilience
In conclusion, Byzantine Fault Tolerance models represent a crucial link to achieving resilience in distributed systems. From classic models like Paxos and PBFT to the advancements in asynchronous BFT and hybrid approaches, these models ensure the integrity and security of networks, particularly in the context of blockchain technology. As the field evolves, Byzantine Fault Tolerance remains a cornerstone in the quest for secure and reliable distributed systems.