Blockchain Consensus Security: Safeguarding the Future of Decentralization
Ensuring the Foundation: Introduction to Blockchain Consensus Security
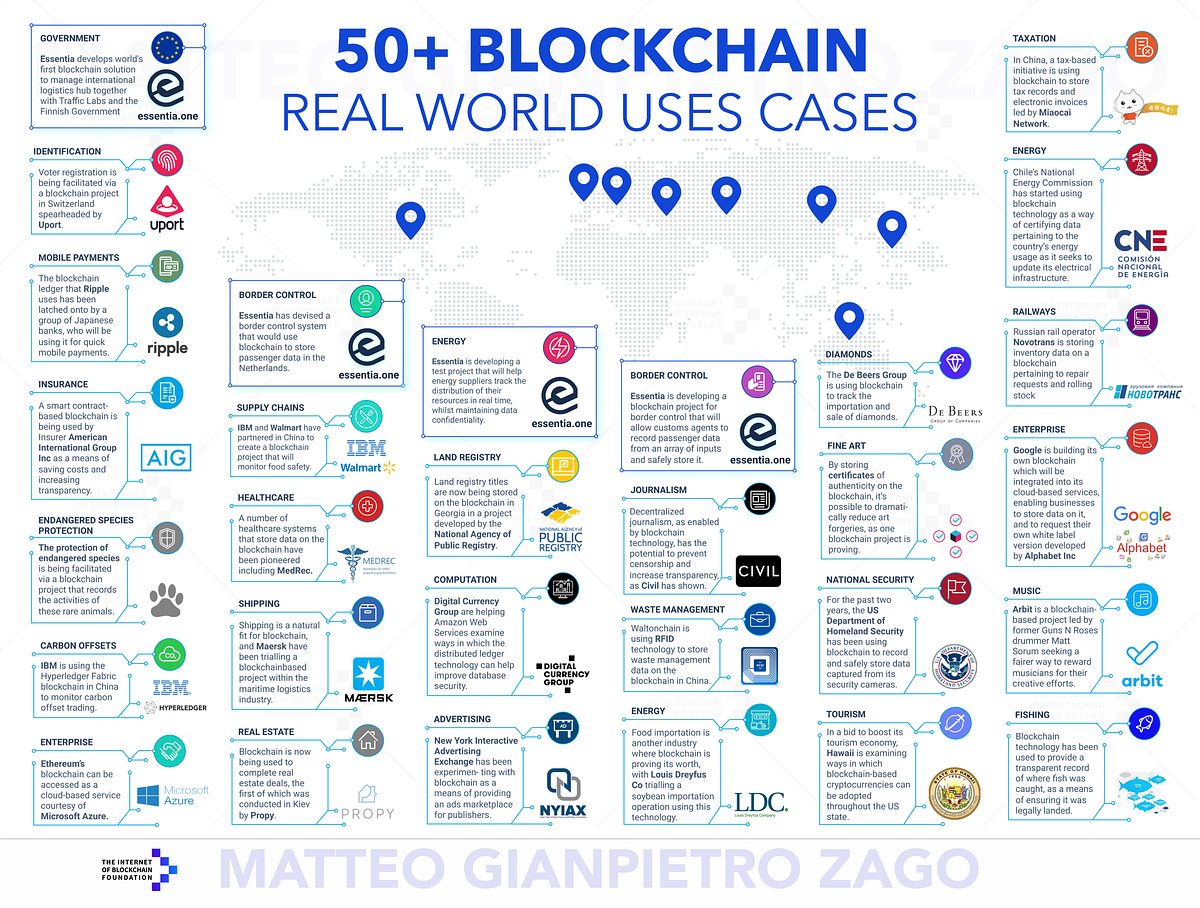
Blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of decentralized systems, providing transparency and security. At the core of blockchain’s reliability lies the concept of consensus security. This article explores the significance of consensus mechanisms in safeguarding the integrity of blockchain networks.
The Pillars of Decentralization: Understanding Blockchain Consensus
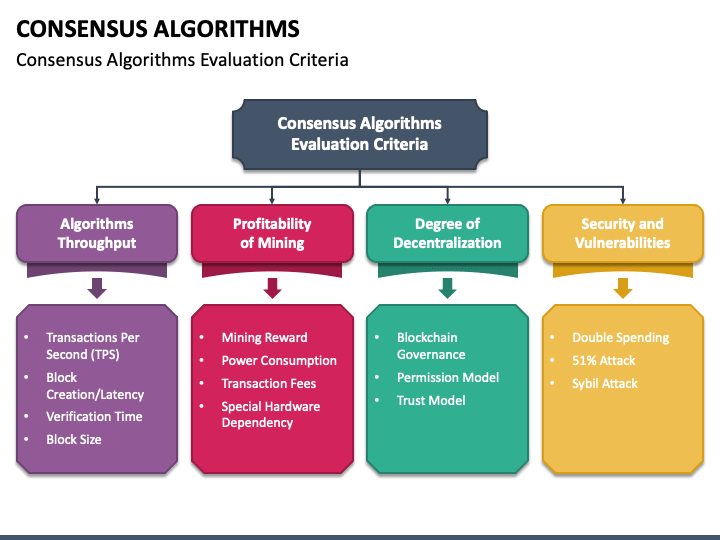
Blockchain consensus is the process by which all participants in a network agree on the state of the system. Various consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), form the backbone of blockchain networks. These mechanisms ensure that transactions are valid and secure, contributing to the overall stability of the decentralized ecosystem.
Proof of Work: Fortifying Blockchain Consensus through Computation
In a Proof of Work consensus model, participants, known as miners, compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first to solve the puzzle adds a new block to the blockchain, validating transactions. While PoW has been instrumental in securing networks like Bitcoin, it requires substantial computational power, raising concerns about energy consumption.
Proof of Stake: Shifting the Paradigm in Blockchain Security
Proof of Stake represents an alternative approach to consensus security. Here, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. PoS is considered more energy-efficient compared to PoW, offering a sustainable solution to blockchain security challenges.
Consensus Failures: Addressing Vulnerabilities in Blockchain Networks
Despite the robustness of consensus mechanisms, no system is entirely immune to vulnerabilities. Consensus failures, such as 51% attacks, can compromise the security of a blockchain network. Understanding these potential pitfalls is crucial for developers and participants in the blockchain space to implement proactive security measures.
The Evolution of Blockchain Security: Innovations and Adaptations
As the blockchain landscape continues to evolve, so do the approaches to consensus security. New consensus models, such as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), aim to address the limitations of earlier mechanisms. These innovations contribute to creating more resilient and secure decentralized networks.
Ensuring Trust in the Digital Age: Blockchain Consensus Applications
Beyond cryptocurrency, blockchain consensus security finds applications in various sectors. From supply chain management to healthcare and finance, the ability to establish trust without relying on central authorities makes blockchain an attractive solution. Consensus security is the linchpin that allows these applications to flourish in the digital age.
The Imperative Link: Blockchain Consensus Security in Action
To witness the impact of blockchain consensus security firsthand, one can explore platforms that prioritize robust mechanisms. Blockchain Consensus Security is a crucial aspect, ensuring the reliability and trustworthiness of transactions. This link provides a deeper understanding of how consensus security functions as the cornerstone of a secure and decentralized digital infrastructure.
Conclusion: Nurturing the Future of Blockchain Consensus Security
In conclusion, the role of consensus mechanisms in blockchain security cannot be overstated. From the foundational principles of PoW and PoS to emerging innovations, consensus security shapes the future of decentralized systems. As the technology advances, fostering a secure and trustworthy blockchain ecosystem becomes paramount for realizing the full potential of the decentralized revolution.